Fig. 4a–f.
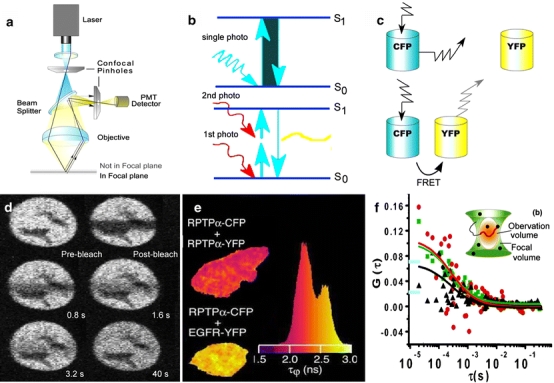
Fluorescent OMI approaches. a LSCM only collects in-focus emitted light. b The principle of multiple photon excitation is based on the use of pulsed long excitation wavelengths to excite fluorescence. c FRET occurs between a donor and an acceptor that are in molecular proximity if the emission spectrum of the donor overlaps the excitation spectrum of the acceptor. d FRAP can reveal the mobility of FP-labeling proteins. These images illustrate the change in fluorescence of cells expressed with YFP-hGR before and after photobleaching. Reproduced from [51] with permission. e FLIM can measure the time-dependent emission intensity. The histogram represents the fluorescence lifetime distributions for the donor in the presence of interactions (red) or not (yellow). Reproduced from [57] with permission. f FCS can monitor the fluorescence signals emitted from the ROI. The cross-correlation curve (black) indicates a higher level of dimer or oligomer formation in the R1- and R5-expressing cells. Reproduced from [59] with permission
