Fig. 6a–d.
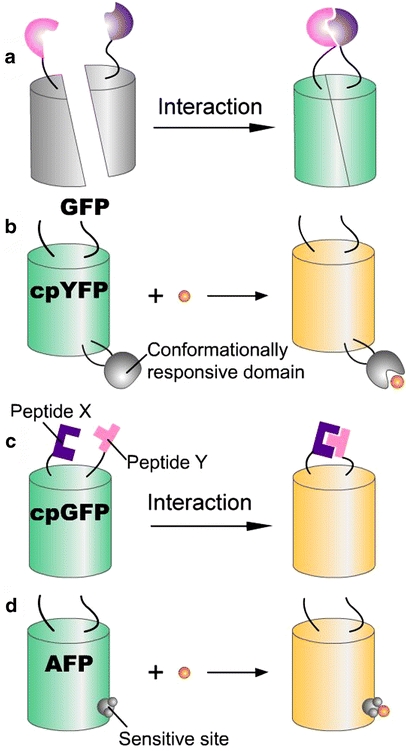
Single FP-based fluorescent probes. a The probe consists of the fusion of two interacting proteins to two complementary fragments of one FP, respectively, which can interact and reinvoke the fluorescence. b Insertion of a conformationlly responsive domain/protein into cpYFP can lead to a change of fluorescence when its conformation is changed. c The probe consists of the fusion of two interacting proteins/domains to the amino and carboxyl termini of cpGFP, which can interact and change the cpGFP fluorescence. d By using mutagenesis, AFP can be engineered to be directly sensitive to a small molecule, such as Cl−, H+
