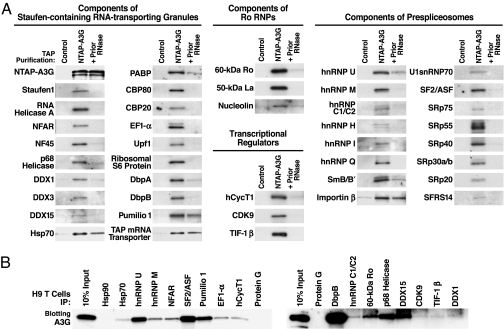
Fig. 2.
Verifying the tandem MS-identified protein cofactors. (A) Purified complexes (NTAP–A3G) or control purifications (unlinked NTAP plus HA–A3G) were immunoblotted with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins. To test RNase A sensitivity of cofactor binding, lysates were pretreated with 50 μg/ml RNase A (+Prior RNase) for 2 h at 4°C before purification. Shown are 42 representative components of Staufen-containing RNA-transporting granules, Ro RNPs, transcriptional regulators, and prespliceosomes. Some cofactors (e.g., Hsp70, Pumilio 1, TAP mRNA transporter, and importin-β) were detected after RNase treatment, suggesting RNA-independent interactions with A3G. Several multifunctional proteins, including nucleolin, DbpB, RNA helicase A, NFAR, and E1B–Ap5, participate in more than one RNP. (B) Endogenous A3G in H9 T cells assembles into the same RNPs. IP analyses were performed with antibodies reacting with select components of the various RNPs identified in HMM A3G complexes followed by rabbit (Left) or mouse (Right) anti-A3G blotting. IP with protein G-agarose or antibodies reacting with Hsp90, an abundant protein not copurifying with NTAP–A3G, were included as negative controls. Fig. 8 provides data on the IP efficiency of each antibody.