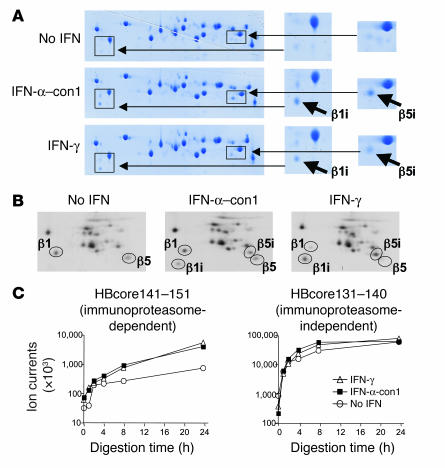
Figure 2. Type I IFN–induced immunoproteasomes exhibit the typical structure and function of IFN-γ–induced immunoproteasomes.
(A) Huh-7 cells were treated with 3 ng/ml IFN-α–con1 or 10 ng/ml IFN-γ for 36 hours, and the 20S proteasome complex was biochemically isolated from cell lysates. Isolated 20S proteasomes were analyzed by 2-dimensional gel electropheresis and Coomassie blue staining. The locations of β1i and β5i are indicated in the insets to the right (magnification, ×2). (B) Huh-7 cells were treated with 3 ng/ml IFN-α–con1 or 10 ng/ml IFN-γ for 36 hours and labeled with 35S-methionine. The 20S proteasome complex was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by 2-dimensional gel electropheresis and autoradiography. The locations of β1, β5, β1i, and β5i are indicated. (C) Biochemically isolated 20S proteasome complexes as shown in A were subsequently incubated with the precursor substrate HBcore131–162 for the indicated time periods. In vitro digests were analyzed by HPLC and mass spectrometry at the indicated time points for the presence of the β5i-dependent HBcore141–151 and the β5i-independent HBcore131–140. Type I IFN–induced immunoproteasomes displayed β5i-dependent proteolytic activity.