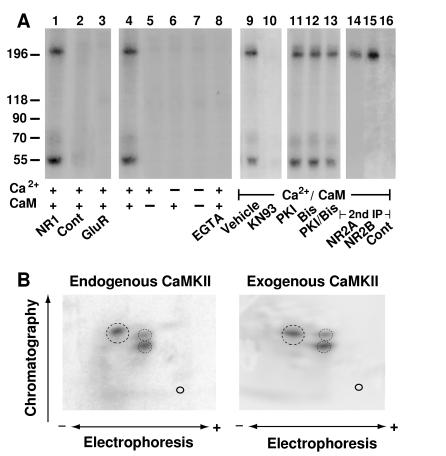
Figure 1.
CaMKII activity is associated with NMDA receptors. (A) NMDA receptor complexes were extracted with 1% deoxycholate from crude rat forebrain membrane fractions, and immunoprecipitations were performed with the NR1-specific antibody αNR1 (lanes 1 and 4–16), control mouse IgG (lane 2), or αGluR1 for precipitation of AMPA receptors (lane 3). Immunocomplexes were incubated in phosphorylation buffer containing Ca2+, calmodulin, EGTA (1 mM), KN93 (50 μM), PKI (1 μM), or the bisindolylmaleimide GF109203X (Bis; 1 μM) as indicated. Samples were either subjected directly to SDS/PAGE (lanes 1–13) or dissociated with SDS before a second immunoprecipitation with the antibodies specific for NR2A or 2B or with control rabbit antibodies was performed (lanes 14–16). Phosphorylated polypeptides were detected by autoradiography. Positions of marker proteins are indicated on the left (in kDa). Similar results were obtained in three different experiments. (B) For phosphopeptide mapping of the NR2B subunit phosphorylated by endogenous kinase (Left), NMDA receptors were solubilized, phosphorylated, and dissociated with SDS before reprecipitation of NR2B and SDS/PAGE. To obtain phosphopeptide maps of NR2B phosphorylated by exogenous CaMKII (Right), crude rat forebrain membrane fractions were extracted with SDS. NR2B was immunoprecipitated and phosphorylated with recombinant CaMKII before SDS/PAGE. Of note, no endogenous kinase activity was detectable when NR2B was immunoprecipitated after dissociation with SDS (see Fig. 3A, lane 9). Tryptic two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps were produced in three independent experiments. Main phosphopeptides are circled.