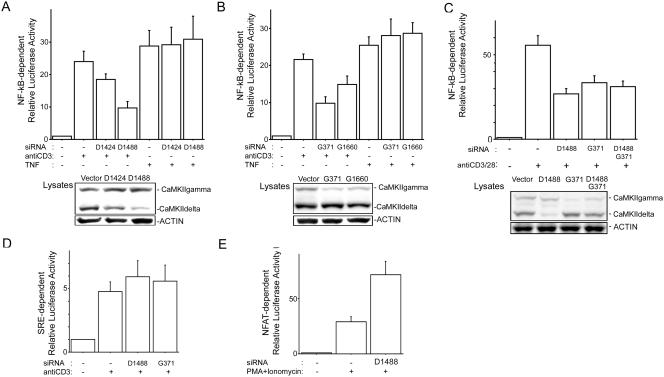
FIG. 3.
siRNAs of CaMKII interfere with NF-κB activation induced by TCR stimulation. (A and B) Jurkat cells were electroporated with 10 μg of siRNA construct (vector, D1424, D1488, G371, or G1660), NF-κB reporter, and pRL-TK construct. Three days later, the cells were incubated with anti-CD3 antibody (1 μg/ml) or TNF-α (1 ng/ml) for 6 h, and then luciferase activities were determined as described in the text. (C) Jurkat cells were electroporated with 10 μg of siRNA construct (vector, D1488, or G371) or 5 μg of D1488 and 5 μg of G371, NF-κB reporter, and pRL-TK. Three days later, the cells were incubated with anti-CD3 antibody (1 μg/ml) or anti-CD28 antibody (0.2 μg/ml) for 6 h, and then luciferase activity was determined. (A to C, lower panels) Equal amounts of protein from lysates used for luciferase assays were blotted for CaMKII and actin. (D) Jurkat cells were electroporated with siRNA construct (vector, D1488, or G371), SRE reporter, and pRL-TK construct. Three days later, the cells were incubated with anti-CD3 antibody (1 μg/ml) for 6 h, and then SRE reporter activity was determined. (E) Jurkat cells were electroporated with siRNA construct (vector or D1488), NFAT reporter, and pRL-TK construct. Three days later, the cells were incubated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) (50 ng/ml) plus ionomycin (1 μM) for 6 h, and then NFAT reporter activity was determined. For results in all panels, four independent experiments were performed. Bars represent standard errors.