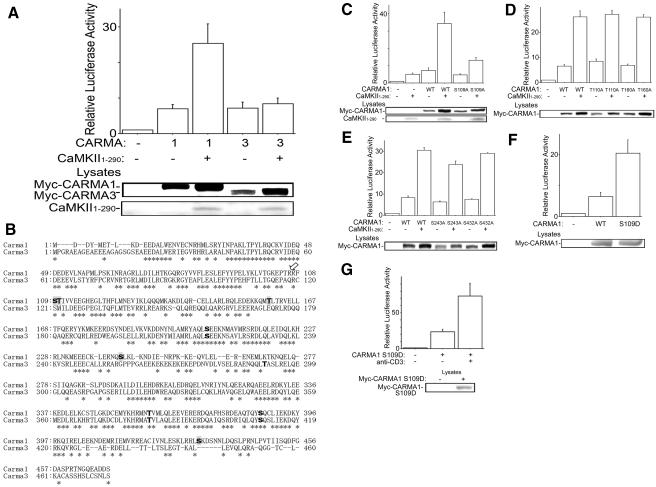
FIG. 5.
Synergistic NF-κB activation of CaMKII with CARMA1 but not with CARMA3. (A) Jurkat cells were electroporated with NF-κB-dependent reporter, pRL-TK construct, 2 μg of CaMKII1-290, and 50 ng of Myc-CARMA1 or Myc-CARMA3. The total amount of DNA was equalized with empty vector. One day later, luciferase activities were determined as described in the text. (B) The Motif Scan program Scansite predicted amino acid residues phosphorylated with CaMKII in the N-terminal regions of CARMA1 and CARMA3 (boldface type). The residues predicted specifically in CARMA1 are shaded. Asterisks indicate residues conserved between CARMA1 and CARMA3. The arrow indicates the P-3 position of CARMA1 Ser109 or CARMA3 Ser121, where CaMKII prefers Arg or Lys for substrates. (C) Jurkat cells were electroporated with NF-κB reporter, pRL-TK construct, 2 μg CaMKII1-290, and 50 ng of Myc-CARMA1 or its mutant with the S109A mutation. The total amount of DNA was equalized with empty vectors. One day later, luciferase activities were determined. (D and E) Results are from an experiment similar to that described for panel C, except with Myc-CARMA1 or its mutant with the (D) T110A or T160A mutation or the (E) S243A or S432A mutation. The total amount of DNA was equalized with empty vectors. One day later, luciferase activities were determined. (F) Jurkat cells were electroporated with NF-κB reporter, pRL-TK construct, and 100 ng of Myc-CARMA1 or its mutant with the S109D mutation. One day later, luciferase activities were determined. (G) Results are from an experiment similar to that described for panel F, except that 18 h later, the cells were incubated with anti-CD3 antibody (1 μg/ml) for a further 6 h, and then luciferase activities were determined. (Lower panels) Cell lysates were blotted with anti-Myc antibody or rabbit anti-CaMKII antibody. Four independent experiments were performed. Bars represent standard errors. WT, wild type.