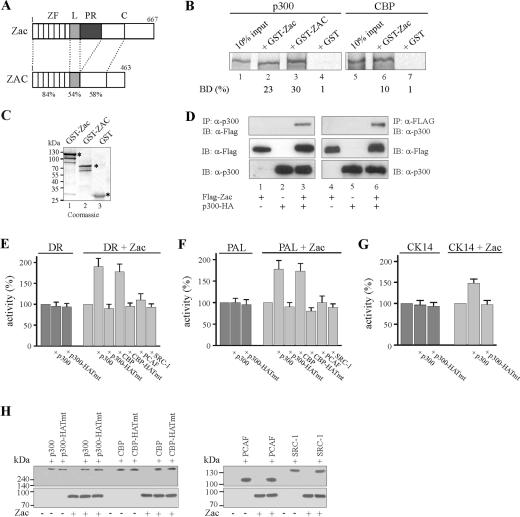
FIG. 1.
p300/CBP enhance Zac transactivation. (A) Scheme of Zac proteins. Numbers denote amino acids, and domains are boxed. Mouse Zac and human ZAC protein contain virtually identical zinc finger domains (ZF) and a strongly conserved linker (L) and N-terminal region within the C terminus (C), whereas the central proline-rich transactivation domain (PR) is specific to mice. Identity (%) is indicated. (B) Pulldown assay. Equal amounts of in vitro-translated p300 or CBP were incubated with adjusted amounts of GST-Zac, GST-ZAC, or GST alone. The fraction of the input (100%) bound by each GST protein [BD (%)] is indicated. (C) The Coomassie blue stain shows adjusted amounts of GST-Zac, GST-ZAC, or GST used in pulldown assays. Asterisks mark bands of predicted molecular mass (kDa). (D) Coimmunoprecipitation experiment. Zac (0.5 μg of pRK7Flag-Zac) and p300 (3 μg of pCMV-p300-HA) were cotransfected in 293T cells as indicated in the text. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting (IB) were done with anti-Flag and anti-p300 antibodies. (E to G) Reporter assays. Zac (0.1 μg of pRK7Flag-Zac) was cotransfected with the DR element, PAL element, and cytokeratin 14 promoter (CK14) (2 μg each) in the absence (dark gray) or presence (light gray) of Zac. Activity of the reporter alone was set to 100% and compared to cotransfection of p300 or the p300 HAT-deficient mutant (p300-HATmt). Activity of the reporter in the presence of Zac was set to 100% and compared to the activity in the presence of wild-type p300, CBP, PCAF, SRC-1, or HAT-deficient mutants (1 μg each). (H) Immunoblot. Expression of Zac (0.1 μg of pRK7Flag-Zac) in the presence or absence of coactivators (1 μg each) as indicated. Coexpressions did not alter Zac or coactivator protein levels. Antibodies were anti-p300 (sc-584), anti-CBP (sc-369), anti-SRC (sc-8995), anti-Flag (F3165), and anti-Zac.