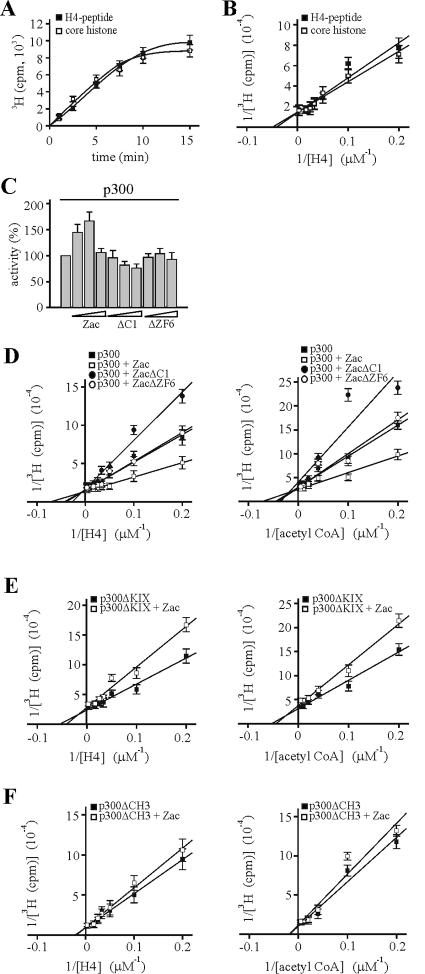
FIG. 10.
Coordinated Zac binding regulates in vitro p300-HAT substrate affinities. Data represent means and standard deviations from at least three experiments done in duplicate. (A) Kinetic analysis of acetylation reaction. Saturating amounts of core histones, H4 peptide, and [3H]acetyl-CoA were incubated with in vitro-translated p300. 3H acetylation was measured for the indicated times. (B) Various concentrations of core histones and H4 peptide were assayed with in vitro-translated p300 and saturating concentrations of [3H]acetyl-CoA. (C) Zac or derivatives dose-dependently regulate p300-HAT activity. p300 (1 nM) was incubated for 2 min with saturating amounts of substrates and with differing concentrations of recombinant Zac, ZacΔC1, or ZacΔZF6 at a ratio of 3:1, 1:1, or 1:3, respectively. (D) Saturation analysis. p300 (1 nM) was incubated for 2 min with differing concentrations of H4 peptide (left) and acetyl-CoA (right) in the absence or presence of equimolar amounts of recombinant Zac, ZacΔC1, or ZacΔZF6. All reactions contained the DR element. Acetylation products and substrate concentrations were plotted in a double-reciprocal graph. (E and F) p300ΔKIX and p300ΔCH3 (1 nM each) were tested as detailed for panel D in the absence or presence of equimolar amounts of Zac.