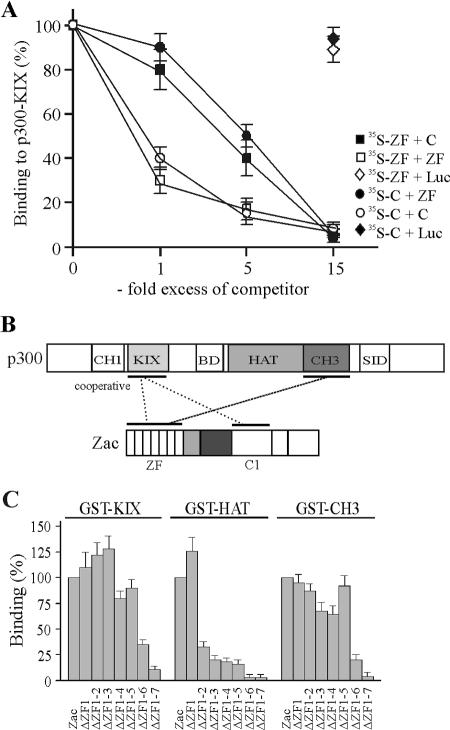
FIG. 4.
Zinc fingers interact cooperatively and selectively with p300. (A) In vitro competition experiment. Binding of the in vitro-translated zinc fingers to GST-KIX (aa 566 to 650) protein was competed by the indicated amounts of in vitro-translated C terminus (C) or by itself. Similarly, binding of the in vitro-translated C terminus was competed by the indicated amounts of in vitro-translated zinc fingers or by itself. In control experiments, a 15-fold excess of in vitro-translated luciferase (Luc) protein failed to compete binding of the zinc fingers (open diamonds) or of the C terminus (filled diamonds) to the KIX domain. (B) Model of Zac-p300 interaction. Zinc fingers and C1 region cooperatively bind to the KIX domain. The zinc fingers additionally bind to the CH3 domain. SID, steroid receptor interacting domain; BD, bromodomain. (C) Pulldown assays. Zac and successive deletion mutants of the zinc fingers were in vitro translated and tested for binding to GST fusions of the KIX, HAT, or CH3 domains. Zac binding was set to 100%.