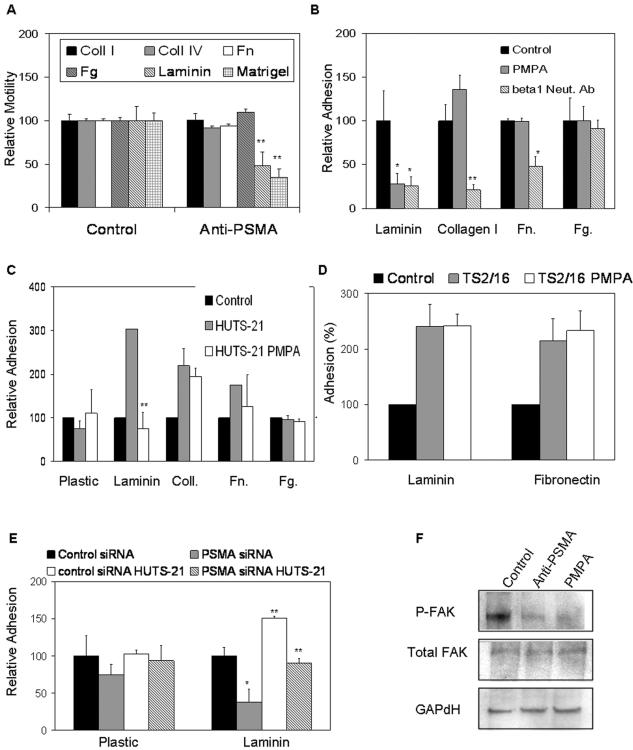
FIG. 3.
PSMA increases β1 integrin signaling in endothelial cells. (A) PSMA-dependent in vitro motility of HUVECs is specifically mediated through laminin (n = 3; P = 0.005) but not other matrix proteins. (B) PSMA antagonists inhibit basal adhesion of HUVECs to laminin equally as well as neutralizing β1 antibodies (Neut. Ab) do, but have no significant effect on binding to fibrinogen, fibronectin, or collagen. (C) Inhibition of PSMA interferes with activated β1 integrin (activated with HUTS-21 antibody) binding to laminin but not other substrates (n = 3; P = 0.002). (D) PSMA inhibition in the presence of the consitutively activating β1 antibody TS2/16 does not alter adhesion to laminin or fibronectin. (E) HUVECs transfected with siRNA targeted against PSMA show reduced basal (n = 3; P = 0.028) and β1-mediated (n = 3; P = 0.001) adhesion compared to that of cells transfected with control siRNA; (F) HUVECs treated with PMPA or anti-PSMA antibody have decreased levels of phosphorylated FAK. *, 0.05 < P > 0.01; **, 0.01 < P > 0.001. Error bars indicate standard deviations.