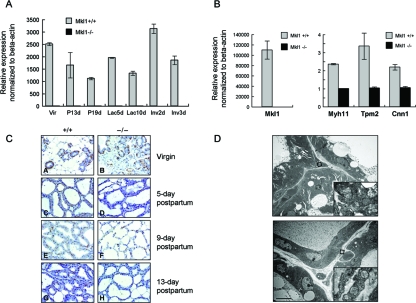
FIG. 7.
Muscle-specific gene expression is markedly reduced in Mkl1−/− mammary glands. (A) Total RNAs were extracted from Mkl1+/+ and Mkl1−/− mammary glands at the indicated times during the reproductive cycle, and expression of Mkl1 mRNA was analyzed using real-time PCR and normalized to beta-actin levels. The data illustrated are from three independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations. Vir, virgin mice; P13d, 13-day-pregnant mice; P19d, 19-day-pregnant mice; Lac5d, 5-day-postpartum mice; Lac10d, 10-day-postpartum mice; Inv2d, mice at day 2 of involution; Inv3d, mice at day 3 of involution. (B) Myoepithelial cells were isolated from day 5 postpartum mammary glands of Mkl1−/− and wild-type females, and total RNAs were extracted. The expression levels of the mRNAs for Mkl1 (left panel), Myh11, Tpm2, and Cnn1 (left panel) were quantified using real-time PCR analysis and normalized to beta-actin transcription levels. Note that the normal level of Mkl1 transcription is very high (∼60-fold) in the myoepithelial cells (B, left panel) compared to the mammary gland tissue as a whole (panel A, Lac5d). (C) SMA staining of the myoepithelial cells of Mkl1−/− and wild-type mammary glands is markedly diminished in the tissues lacking Mkl1. (D) Myoepithelial cells from Mkl1−/− (lower panel) and wild-type (upper panel) mammary glands were examined by electron microscopy. Boxes overlie the myoepithelial cells and represent areas shown in higher magnification to demonstrate the abnormal morphology of the mitochondria in the Mkl1−/− cells, which is similar to that observed in Mkl1−/− cardiac muscle (Fig. 2B).