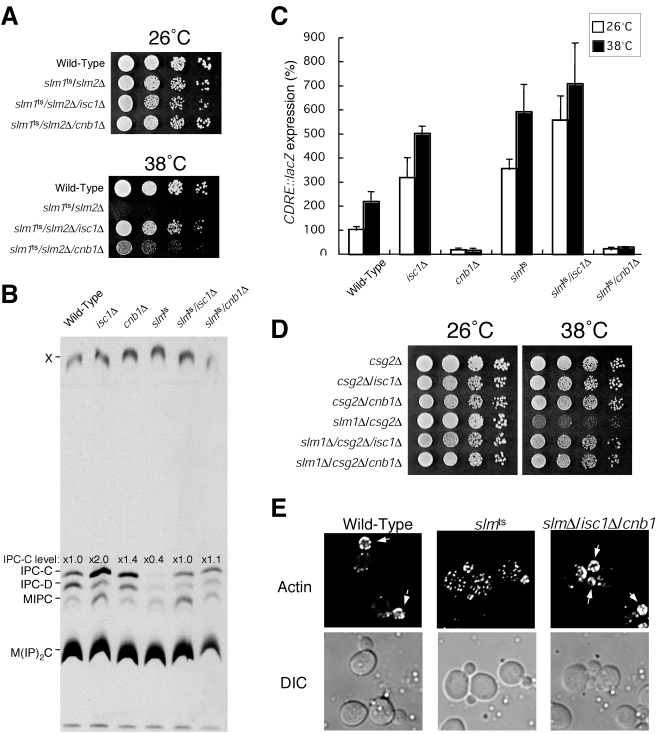
FIG. 8.
Deletion of ISC1 or CNB1 suppresses the phenotypes associated with loss of Slm1 and Slm2 function. (A) Wild-type and slm1ts/slm2Δ, slm1ts/slm2Δ/isc1Δ, and slm1ts/slm2Δ/cnb1Δ mutant cells were grown on YPD at 26°C or 38°C for 2 days. (B) Wild-type, isc1Δ, cnb1Δ, and slm1ts/slm2Δ, slm1ts/slm2Δ/isc1Δ and slm1ts/slm2Δ/cnb1Δ′ cells were metabolically labeled with [3H]serine for 6 h. Sphingolipids were analyzed by TLC. (C) Wild-type, isc1Δ, cnb1Δ, slm1ts/slm2Δ, slm1ts/slm2Δ/isc1Δ and slm1ts/slm2Δ/cnb1Δ cells carrying the 4× CDRE-lacZ reporter plasmid (AMS366) were grown to log phase at 26°C and shifted to 38°C for 2 h, and β-galactosidase activity was determined. The data shown represent the means ± standard errors of the means of results from three independent experiments. (D) csg2Δ, csg2Δ/isc1Δ, csg2Δ/cnb1Δ, slm1Δ/csg2Δ, slm1Δ/csg2Δ/isc1Δ, and slm1Δ/csg2Δ/cnb1Δ cells were grown on YPD at 26 or 38°C for 2 days. (E) Wild-type, slm1ts/slm2Δ and slm1Δ/slm2Δ/isc1Δ/cnb1Δ cells were shifted to 38°C for 2 h, fixed, stained with rhodamine-phalloidin, and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. DIC, differential interference contrast.