FIG. 5.
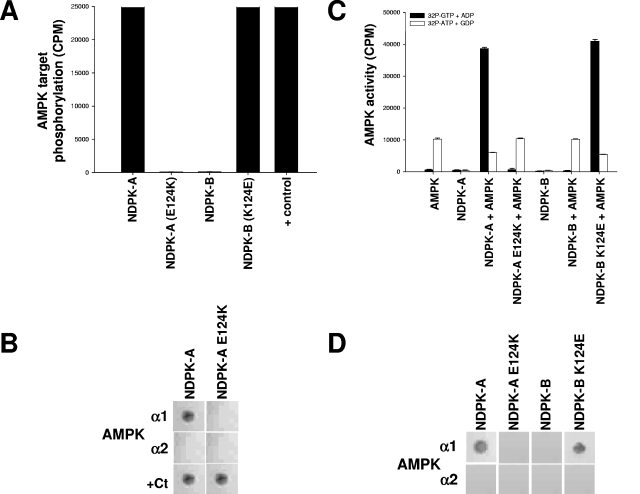
A single amino acid on NDPK-A determines its association with AMPK α1. (A) Pure, active rat liver AMPK was used to phosphorylate a selection of substrates, 15 μg (each) of NDPK-A, NDPK-A(E124K), NDPK-B, and NDPK-B(K124E). In the final lane, CK2α holoenzyme (+ control) was used to phosphorylate NDPK-A (shown) and NDPK-B (not shown) mutant recombinant proteins, and both were identical. (B) NDPK-A and NDPK-A E124K mutant recombinant proteins were immobilized on nitrocellulose membranes and then blocked/washed as described above for the Western blot protocol. Furthermore, 10 μg of purified, recombinant AMPK α1, AMPK α2, or CK2α protein was overlaid onto the membrane, with binding detected using isoform-specific antibodies for each protein, as described above for the Western blot protocol. (C) Substrate-channeling ability of NDPK mutants was tested by adding, where indicated, active rat liver AMPK to 15 μg of either NDPK-A, NDPK-A E124K, NDPK-B, or NDPK-B K124E recombinant protein. Either [32P]GTP plus ADP (resulting in labeled NDPK-generated ATP) or [32P]ATP plus GDP (resulting in labeled NDPK-generated GTP) was used to demonstrate substrate channeling or substrate stealing, respectively, and also to act as cross-contamination control for each kinase individually. (D) NDPK-A, NDPK-A E124K, NDPK-B, and NDPK-B K124E proteins were immobilized on nitrocellulose membranes and then blocked/washed as described above for the Western blot protocol. Furthermore, 10 μg of purified, recombinant AMPK α1 or AMPK α2 protein was overlaid onto the membrane, with binding detected using isoform-specific antibodies for each protein, as described above for the Western blot protocol.