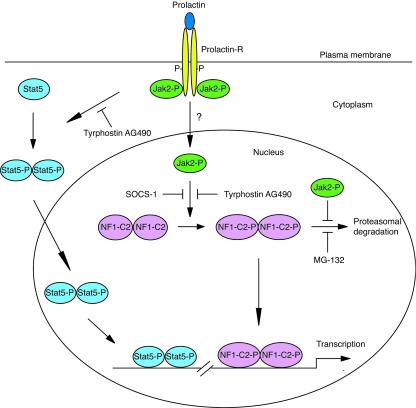
FIG. 9.
Mechanisms for prolactin action in the mouse mammary gland. The novel mechanism proposed by us is that prolactin/prolactin receptor (Prolactin-R) activates Jak2, which translocates to the nucleus by an as-yet-unknown mechanism. In the nucleus, Jak2 tyrosine phosphorylates (P) the transcription factor NF1-C2 and protects it from proteasomal degradation. The classical way by which prolactin transduces its signal in mammary gland is through the depicted Jak2-Stat5 pathway. When prolactin binds to its receptor, the receptor dimerizes and Jak2 is activated by transphosphorylation. Jak2 mediates phosphorylation of Stat5, which dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus, where it activates target genes.