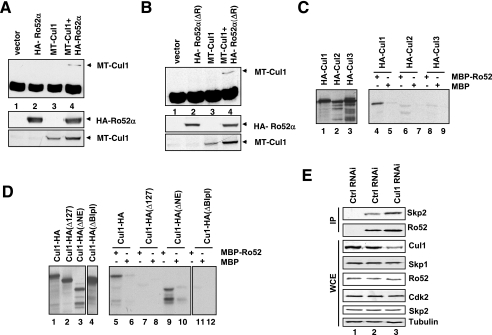
FIG. 4.
Cul1 interacts with Ro52 via the cullin homology domain. (A) HA-Ro52α and MT-Cul1 were expressed individually or together in HeLa cells, and aliquots of lysates were either subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA 12CA5 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with rabbit anti-Cul1 antibody (upper panel), or directly processed for immunoblotting with anti-HA MAb HA11 (middle panel) or anti-Myc MAb 9E10 (lower panel). (B) The panel shown is as described for panel A, except that HA-Ro52α(ΔR) lacking the RING domain was transfected instead of HA-Ro52α(wt). (C) IVTs of HA-Cul1, HA-Cul2, or HA-Cul3 were incubated with MBP (lanes 5, 7, and 9) or MBP-Ro52 (lanes 4, 6, and 8) fusion proteins, and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (lanes 2 through 4). Lanes 1 to 3, input IVTs. −, presence of; +, absence of. (D) IVTs of Cul1-HA, Cul1-HA(Δ127), Cul1-HA(ΔNE), or Cul1-HA(ΔBlpI) were incubated with MBP (lanes 6, 8, 10, and 12) or MBP-Ro52 (lanes 5, 7, 9, and 11) fusion proteins, and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (lanes 2 through 4). Lanes 1 to 4, input IVTs. −, presence of; +, absence of. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs corresponding to either nonrelevant mRNA (control; lanes 1 and 2), or Cul1 mRNA (lane 3). Aliquots were processed for immunoprecipitation (IP) with either control IgG (lane 1) or anti-Ro52 MAb (lanes 2 and 3) that had been covalently coupled to protein A-Sepharose beads using dimethylpimelimidate and processed for immunoblotting using anti-Skp2 MAb mix or anti-Ro52 MAb 83.34. Other aliquots were directly processed for immunoblotting with antibodies directed against indicated proteins. WCE, whole-cell extracts.