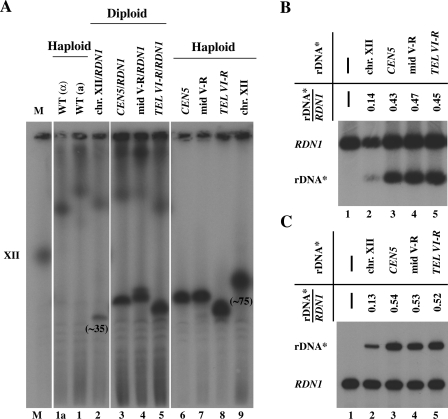
FIG. 7.
Transcription activities of rRNA gene arrays at ectopic sites relative to that at the native site in diploid strains carrying a pair of chromosome XII with or without the native RDN1 and a pair of another chromosome with or without rDNA* array at an ectopic locus. (A) CHEF analysis of diploid strains, NOY2039 (RDN1 together with rDNA* array at the native site), NOY2040 (one rDNA* array near CEN5), NOY2041 (one rDNA* array at mid V-R), and NOY2042 (one rDNA* array near TEL VI-R) (lanes 2 to 5, respectively) and haploid strains used to construct the diploid strains, NOY396, NOY388, NOY2030, NOY2031, NOY2032, and NOY2029 (lanes 1a, 1, 6, 7, 8, and 9, respectively). An autoradiogram after probing with radioactive rRNA gene probe is shown. Chromosome XII carrying an rDNA* array in NOY2029 (lane 9) and that in diploid NOY2056 (lane 2) are marked by giving approximate copy numbers below the chromosome bands to indicate a significant alteration in copy numbers upon construction of the diploid strain. (The copy number of rDNA* in such diploid varied depending on the diploid clones analyzed and ranged from ∼35 to ∼98. In diploid cells formed from two haploids, one with high and one with low rDNA repeat numbers at RDN1, by CHEF analysis, the size of chromosome XII derived from the latter is observed to be more homogeneous, i.e., rDNA repeat expansion and contraction appears to be inhibited. A similar phenomenon was previously observed, and a possible explanation was presented [39].) (B) Southern analysis of relative rRNA gene repeat numbers. (C) Primer extension analysis of relative transcription levels. In panels B and C, the diploid strains given in panel A (lanes 2 to 5) and haploid control strain NOY388 (lane 1) were analyzed, and the ratios of the value for rDNA* to that for RDN1 in respective diploid strains are shown.