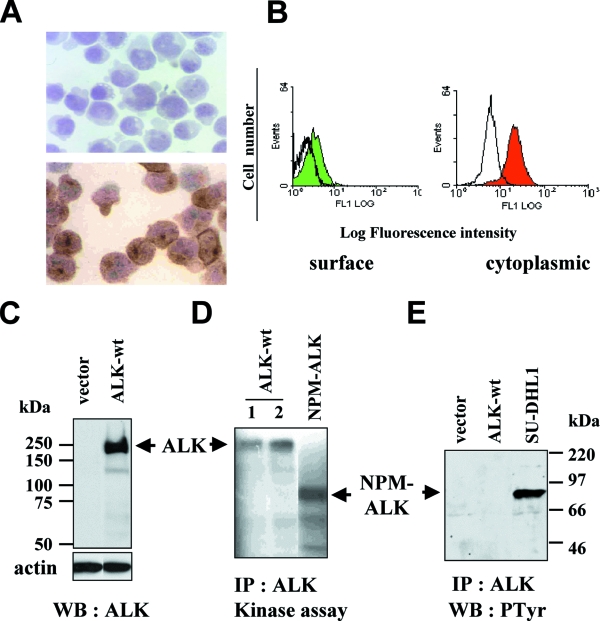
FIG. 1.
Characterization of ALK expressed in stably transfected Jurkat cells. (A) Jurkat cells, transfected with ALK cDNA or with control vector (Jurkat/neo cells), were selected with Geneticin for stable gene expression and cloned by limiting dilution. Jurkat/neo cells (top) or an ALK-transfected Jurkat clone (bottom) were cytospun onto glass slides. Immunohistochemical analysis of the ALK protein was done using the ALK1 MAb with a three-stage immunoperoxidase technique. Magnification, ×800. (B) Intact (left panel) or permeabilized (right panel) Jurkat/ALK cells were stained with the REAB or ALK1 antibodies, followed, respectively, by FITC-coupled goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse Ig. Immunofluorescence analysis of surface (left) and intracellular (right) ALK staining was analyzed by flow cytometry (colored histograms). Background cell fluorescence with an isotypic control antibody is shown as a black line histogram. (C) Fifty micrograms of protein from total cell lysates of Jurkat/neo (vector) or Jurkat/ALK (ALK-wt) cells was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using the ALKc MAb. ALK is detected as a 200-kDa band. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left. The filter was stripped and reprobed using an antiactin MAb to assess comparable loading. (D) In vitro kinase assay of anti-ALK immunoprecipitates from total cell extracts of two ALK-expressing (labeled 1 and 2, ALK-wt) and one NPM-ALK-expressing clone, showing autophosphorylation of the proteins. (E) Cell lysates from vector- or ALK-wt-transfected Jurkat cells and from the NPM-ALK-expressing ALCL cell line SU-DHL1 were immunoprecipitated using the ALK1 MAb and then analyzed through Western blotting using the antiphosphotyrosine MAb 4G10. Tyrosine phosphorylation was detected in NPM-ALK-expressing but not in ALK-expressing cells. Molecular mass markers are indicated.