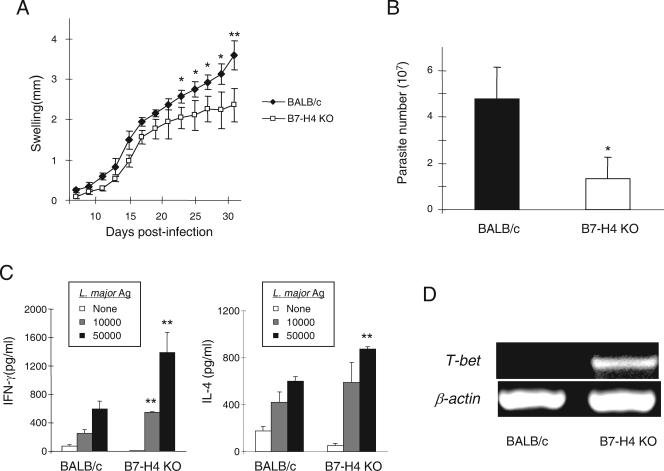
FIG. 3.
Enhanced Th1 responses against L. major in B7-H4 KO mice. (A) Reduced footpad swelling in B7-H4 KO mice. BALB/c or B7-H4 KO mice in a BALB/c background (n = 6) were inoculated in the right hind footpad with L. major promastigotes, and footpad swelling was measured at the indicated time points. Two mice of each genotype died at day 21 and thus were excluded from the experiment. The data shown are the mean ± the standard deviation of footpad swelling and are representative of two independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (Student's t test). (B) Reduced parasite burden in B7-H4 KO mice. The number of L. major promastigotes in the footpad was assessed as described in Materials and Methods at day 14 postinfection. The data shown are the mean ± the standard deviation and are representative of two independent experiments with three mice per genotype. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test. (C) Elevated IFN-γ production by T cells from B7-H4 KO mice. Popliteal LN cells were isolated at day 14 postinfection and then restimulated with or without antigen (Ag) for 3 days. The concentrations of IFN-γ and IL-4 in the culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. The data shown are means ± standard deviations and are representative of two independent experiments with three mice per genotype. **, P < 0.01 by Student's t test compared to data from the WT control at the same dose of antigen. (D) Increased T-bet expression in CD4+ T cells of B7-H4 KO mice. CD4 T cells were purified from popliteal LNs at day 14 postinfection, and the level of T-bet mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. The data shown are representative of three experiments with three mice per genotype.