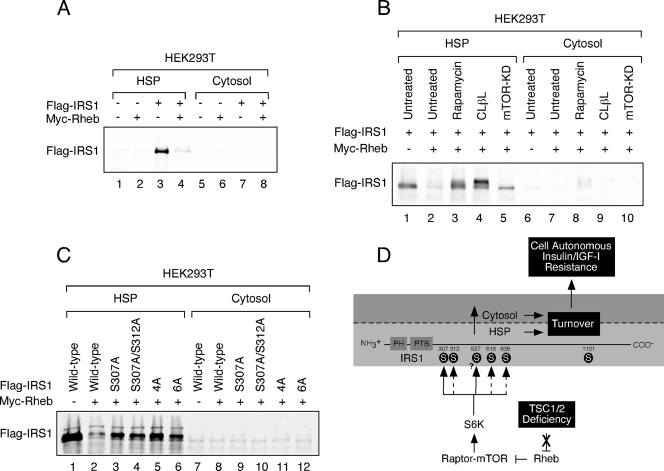
FIG. 4.
IRS1 depletion from the HSP in HEK293T cells. (A) HEK293T cells expressing Flag-IRS1 and/or Myc-Rheb were serum deprived for 4 h and then fractionated and immunoblotted with anti-Flag antibody. (B) HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-IRS1 were cotransfected with empty vector or Myc-Rheb and Myc-mTOR (KD) as indicated. Cells were either left untreated or cultured in the presence 100 nM rapamycin or 5 μM clasto-lactacystin-β-lactone (CLβL) for 48 h. (C) Myc-Rheb was coexpressed with a panel of Flag-IRS1 mutants (defined in the legend of Fig. 2D and 3D) as indicated. The HSP fraction was prepared and immunoblotted with anti-Flag antibodies. The expressions of these mutants are similar at steady state (data not shown). (D) Proposed model for IRS1 regulation in the context of TSC deficiency. When TSC1 or TSC2 is inactivated, signaling through the Rheb/Raptor-mTOR/S6K axis is constitutive. S6K directly phosphorylates IRS1 on the RXRXXS/T site, S307 and potentially S527 (solid arrows) but not S1101. Raptor-mTOR or other kinases phosphorylate IRS1 on the S/T,P sites, S312, S616, and S636/9, which is somehow indirectly regulated by S6K1 (hatched arrows. The phosphorylation of these sites collectively contributes to the depletion of IRS1 from the HSP fraction. This either involves phosphorylation-mediated redistribution of IRS1 from the HSP to the cytosol, where it is subsequently degraded, or degradation directly in the HSP. The mode of IRS1 turnover is likely to be cell type dependent. IRS1 turnover produces cell-autonomous insensitivity to insulin or IGF-I.