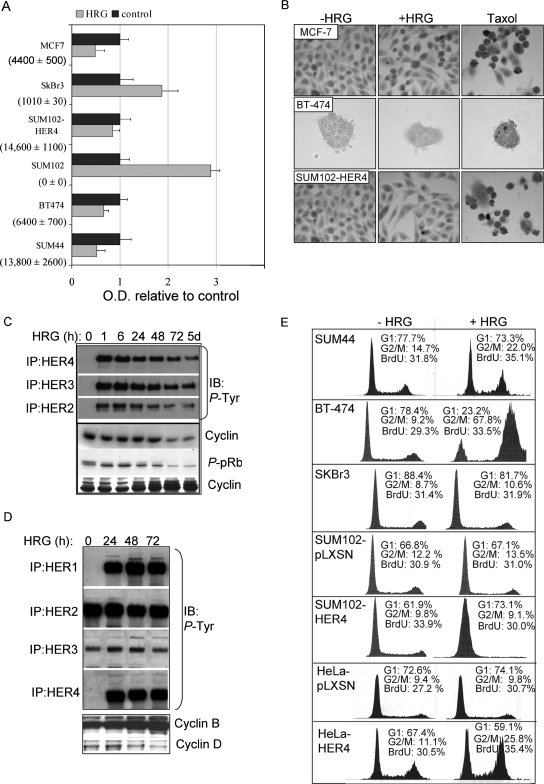
FIG. 1.
HRG-mediated growth inhibition requires HER4 expression. (A) Absolute levels of HER4 mRNA transcripts were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR and are shown for each cell line in parentheses (average number of transcripts ± standard deviation [SD]; n = 3). Equal numbers of cells from each cell line were plated and cultured for 48 h with or without HRG; relative cell numbers were determined by using the MTS assay, which converts cell density to optical density (OD). The values represent the average OD ± SD, represented as a ratio to the OD produced by cells grown in the absence of HRG. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times. (B) In situ TUNEL analysis of HRG-treated MCF-7, BT-474, and SUM44 cells treated with or without HRG for 0 to 48 h. (C and D) Western analysis of whole-cell extracts or HER1, HER2, HER3, and HER4 immunoprecipitates from SUM44 cells (C) or BT-474 cells (D), treated with HRG for the indicated time courses, to detect the expression of cyclin D, cyclin B, or phospho-pRb or phosphotyrosine residues. (E) Cell cycle analysis of cells cultured in serum-free medium with or without HRG for 72 h. The percentages of the cell population in the G1 and G2/M phases of the cell cycle are shown. In addition, cells were labeled with BrdU for 6 h, stained with an FITC-conjugated anti-BrdU antibody, and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentages of BrdU-positive cells are indicated. A total of >10,000 nuclei per sample were counted (n = 3).