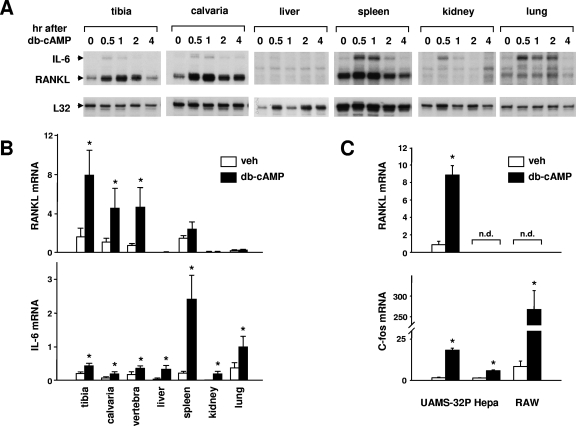
FIG. 1.
Tissue-specific stimulation of RANKL. (A) RNase protection assay of RNA from mice injected with db-cAMP (100 mg/kg body weight). RNA was isolated from the indicated tissues at the indicated time points and analyzed with probes for IL-6, RANKL, and ribosomal protein L32. Each lane contains RNA from a single mouse, and the RNA analyzed in lane 0 is from an uninjected mouse. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RNA from mice injected with PBS (white bars) or db-cAMP at 100 mg/kg body weight (black bars). The indicated tissues were harvested 1 h after injection, and total RNA was prepared. RANKL or IL-6 mRNAs were quantified using Taqman RT-PCR, and the values were normalized to ribosomal protein S2. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of three animals. veh, vehicle. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RNA from cell lines treated with vehicle or 1.5 mM db-cAMP for 24 h. Values for RANKL and c-fos were normalized to ribosomal protein S2. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of triplicate wells. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test versus vehicle. n.d., not detectable.