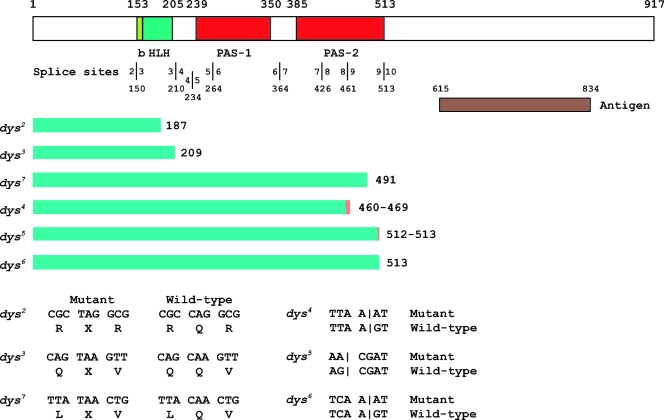
FIG. 3.
Molecular defects of dys mutants. At the top is a schematic of the Dys protein. The basic-region DNA binding domain (b), HLH dimerization domain, and PAS-1 and PAS-2 domains are labeled below the schematic. Above the schematic are the amino acid positions of domain boundaries. The locations of splice sites are shown below the domain names, and each exon-intron boundary is indicated by a vertical line with the corresponding exon indicated on each side, along with the amino acid residue corresponding to the splice site below. The anti-Dys antibody was raised against animals injected with a bacterial fusion protein antigen containing Dys protein residues 615 to 834. The conceptual protein fragment predicted for each dys mutant gene is indicated by a green bar, followed by the size in amino acids. The minimum extent of the predicted protein is shown in green, and the orange bar indicates translated intronic sequences. dys2, dys3, and dys7 have premature termination codons that should result in a truncated protein. dys4, dys5, and dys6 have splice site mutations. dys4 and dys5 are followed by two numbers; the first indicates the end of the exonic sequence and the second the location of the in-frame termination codon in the adjacent intron. The sequence alteration for each mutant is shown at the bottom. Vertical lines for dys4, dys5, and dys6 indicate locations of splice sites.