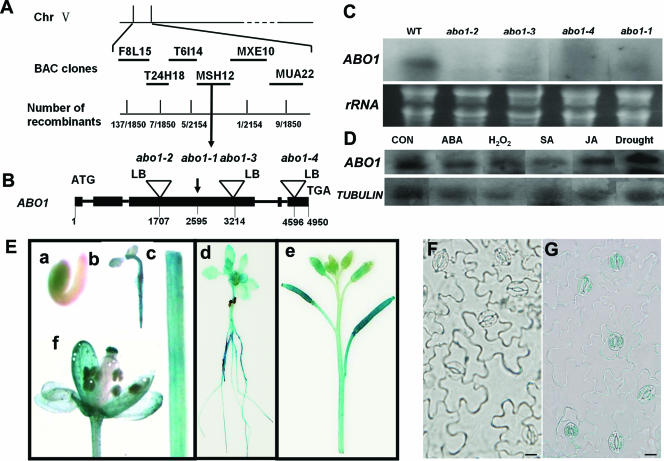
FIG. 8.
Positional cloning and expression pattern of the ABO1 gene. (A) Positional cloning of the ABO1 gene. Chr, chromosome; BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome. (B) Structure of the ABO1 gene, showing the different mutant alleles. LB, T-DNA left border. (C) Expression of the ABO1 gene in different mutant alleles. An rRNA gene was used as a loading control. WT, wild type. (D) ABO1 expression was not induced under different treatment conditions. A tubulin gene was used as a control. Con, seedlings without any treatment; SA, salicylic acid; JA, jasmonic acid. (E) ABO1 promoter-GUS analysis in Arabidopsis transgenic seedlings. (a) One-day-old seedling, (b) 4-day-old seedling, (c) stem, (d) 10-day-old seedling, (e) siliques, and (f) flower. (F) Guard cells on an abaxial epidermis from a nontransgenic plant, used as a negative control. (G) ABO1 promoter-GUS analysis of guard cells on an abaxial epidermis from a transgenic plant. Bar, 10 μm.