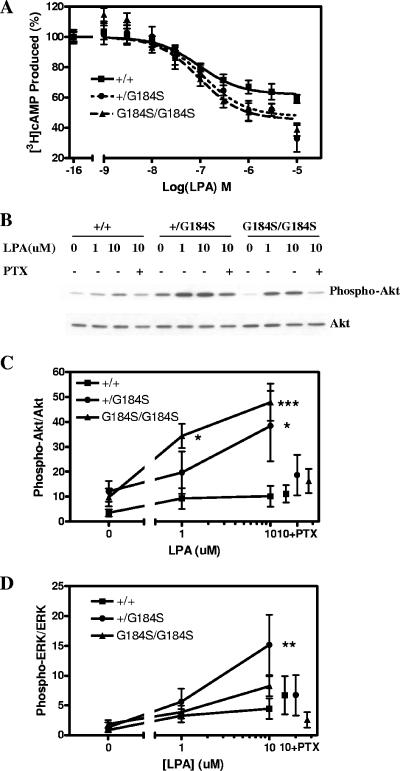
FIG. 2.
Biochemical phenotype of Gαi2G184S mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. (A) Lysophosphatidic acid inhibition of forskolin-stimulated AC. Dose-response curves for inhibition of AC by lysophosphatidic acid were determined from three individual embryonic fibroblast cell lines of each genotype. n = 9 for both +/+ and +/G184S, and n = 6 for G184S/G184S. Maximum inhibition among all three genotypes is different by F-test, P < 0.005. (B) PTX-sensitive phosphorylation/activation of Akt stimulated by LPA. MEF cells were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of LPA for 7.5 min. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with an Akt phospho-specific antibody (Ser473). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with an antibody raised against total Akt. In some samples, the cells were incubated with PTX (100 ng/ml) overnight before stimulation with 10 μM LPA. (C and D) Western blotting and densitometric analysis of activation of Akt (C) and ERK (D) from averages of three independent experiments. The ratios of the densities of phosphorylated Akt or ERK to those for total Akt or ERK were calculated and are means ± standard errors of the means of three experiments. Significant differences from +/+ cells by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest are indicated as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.