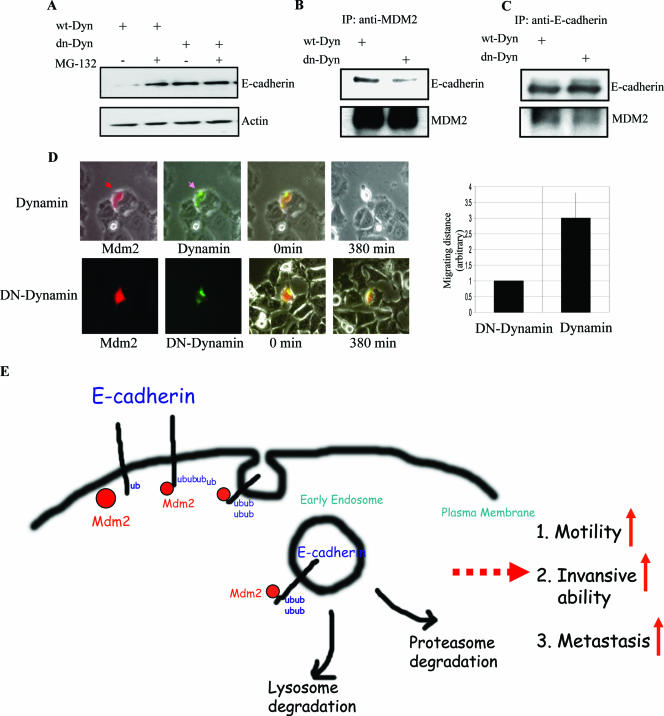
FIG. 7.
An intact endocytic machinery is required for MDM2 association with E-cadherin and regulation of its function. (A) HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with wild-type dynamin (wt-Dyn) or dn-dynamin (dn-Dyn) and lysed following treatment with or without 20 μM MG132 for 4 h. Protein extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B and C) Dominant-negative mutants of dynamin disrupt the interaction between MDM2 and E-cadherin. HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with either the wild type or a dominant-negative mutant of dynamin, and after 48 h, cells were treated with MG132 prior to protein extraction, reciprocal coimmunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) MCF-7 cells were cotransfected with MDM2 expression plasmid and red florescence protein expression plasmid (DsRed) (at a 10:1 ratio) plus pEGFP-dynamin or pEGFP-dn-dynamin. Cells were monitored by time lapse fluorescence microscopy, and photographs were acquired at the indicated times beginning 24 h after transfection. The relative cell migrating distances (arbitrary units) are shown in the right panel. (E) Model proposed to illustrate that E-cadherin degradation by MDM2 is through endocytosis.