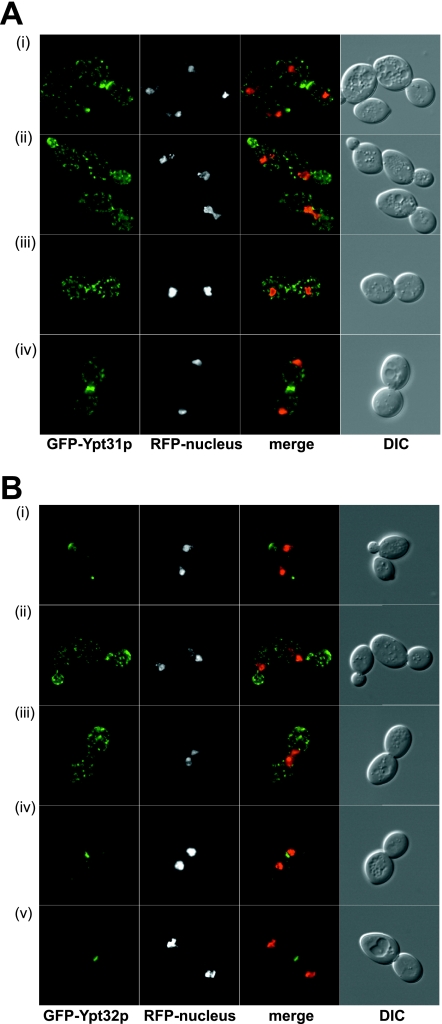
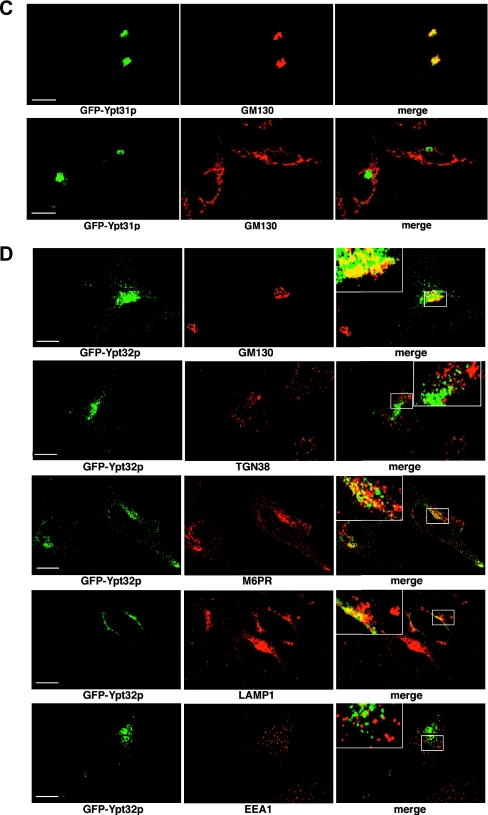
FIG. 5.
Localization of GFP-Ypt31p and GFP-Ypt32p in yeast and HeLa cells. (A) Localization of GFP-Ypt31p in yeast. GFP-Ypt31p-expressing live cells were viewed by fluorescence microscopy. GFP-Ypt31p localization was analyzed at various stages of the yeast cell cycle. A nuclear marker (Gal4BD-RFP) and the relative sizes of the mother and daughter cells were used to ascertain the cell cycle stage. The overlay of the GFP and RFP channels are of the maximum projection of each channel, and differential interference contrast (DIC) images were taken in one z plane. (B) Localization of GFP-Ypt32p in yeast. GFP-Ypt32p was expressed in yeast cells as the only copy, and live cells were viewed by fluorescence microscopy as described for panel A. (C) Localization of GFP-Ypt31p in HeLa cells. GFP-Ypt31p was expressed in HeLa cells, and fixed cells were viewed by confocal microscopy. The GFP fluorescence signal was compared to those of antibody markers for the following cellular compartments: Golgi apparatus (GM130) and trans-Golgi network (TGN38). In each case, a merge of the two fluorescence images is shown. Bars = 10 μm. (D) Localization of GFP-Ypt32p in HeLa cells. GFP-Ypt32p was expressed in HeLa cells, and fixed cells were viewed by confocal microscopy. The GFP fluorescence signal was compared to those of antibody markers for the following cellular compartments: Golgi apparatus (GM130) and trans-Golgi network (TGN38), late endosomes (M6PR), late endosomes/lysosomes (LAMP1), and early endosomes (EEA1). In each case, a merge of the two fluorescence images is shown. Insets show selected areas enlarged approximately threefold, with color levels optimized to show colocalization. Bars = 10 μm.