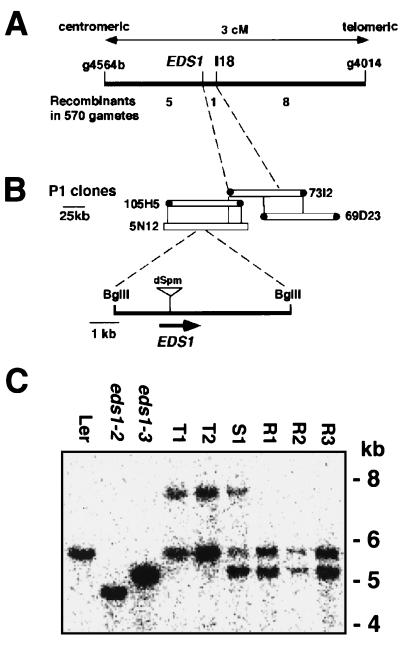
Figure 1.
High-resolution mapping and transposon tagging of EDS1. (A) Genetic map. Recombinant analysis placed EDS1 0.2 cM centromeric to I18, an restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) marker derived from a I/dSpm transposon insertion in Ler. (B) P1 contig. I18 was used to identify two P1 phage clones, 73I2 and 69D23. An RFLP was detected between Ler and Col-0 DNA with the 73I2 centromeric end-probe, allowing orientation of P1 clones relative to EDS1. I/dSpm insertions into EDS1 were located in Ler DNA corresponding to a 5.7-kb internal BglII fragment of P1 clones 105H5 and 5N12. (C) A blot of BglII-digested genomic DNA was probed with a 32P-labeled inverse-PCR product derived from an I/dSpm insertion shared by eds1 lines T1–T5. The blot shows the wild-type Ler 5.7-kb band and deletions of ≈1 or ≈0.5 kb, respectively, in the FN-derived Ler mutants eds1–2 and eds1–3. Lines T1 and T2 possess an additional 7.9-kb band caused by insertion of a 2.2-kb I/dSpm element. In contrast to a Noco2-susceptible F1 plant (S1) derived from a cross between T1 and eds1–3, three independent Noco2-resistant (revertant) F1 plants (R1, R2, and R3) have lost the I/dSpm insertion.