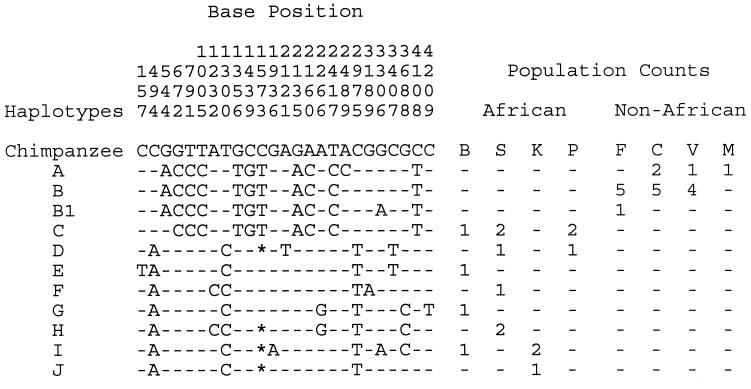
Figure 1.
Polymorphic base positions within humans. Each of the 25 polymorphic positions is listed by its position within the alignment. The base values of the chimpanzee sequences are shown for these positions, and the human haplotypes are shown with respect to the chimpanzee sequences. - indicates the haplotype base was the same as the chimpanzee; ∗ indicates a gap in a sequence relative to the chimpanzee, where a polymorphism fell within an insertion/deletion. The polymorphism at position 2,489 is associated with an amino acid variant (ATG, for methionine, and CTG for leucine). The polymorphism at position 544 is a synonymous variant (GCA and GCG for alanine). All other variants occurred in introns. The haplotype letter designations are the same as those shown in Fig. 2. The B1 haplotype is not included in Fig. 2 because position 3,306 was removed from the genetree analyses of the complete Old World sample (see text). The populations are as follows: B, South African Bantu speakers; S, Senegalese; K, Khoisan from the Angola/Namibia border; P, Pygmy from the Central African Republic; C, China; V, Vietnam; F, France; M, Mongolia. The C, V, and F samples are random subsets of DNAs used in a larger study (45).