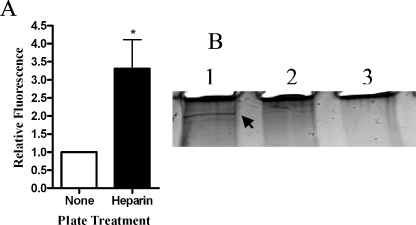
FIG. 8.
H. somus binds to heparin. (A) SYTO-BC Green-labeled H. somnus cells were added to heparin-coated plates incubated for 1 h at 4°C. Uncoated wells were used as a negative control. The plates were washed four times with PBS, and the fluorescence in each well was measured at 495/530 nm. Data are expressed as the ratio of fluorescence units relative to uncoated wells (mean ± SEM of five independent experiments). (B) Heparin-labeled beads were incubated with H. somnus culture filtrates (10 μg) for 1 h at 22°C. Beads that lacked heparin were included as a negative control. The beads were then washed five times with PBS, and the proteins were eluted by boiling in sample loading buffer. The eluted proteins were separated on a 4 to 20% polyacrylamide gel and visualized by silver staining. Lane 1, H. somnus filtrate incubated with heparin-coated beads; lane 2, H. somnus filtrate incubated with control beads; lane 3, heparin-coated bead control. The arrow in lane A indicates a 128-kDa putative heparin-binding protein. Results shown are for one representative experiment from three that were performed.