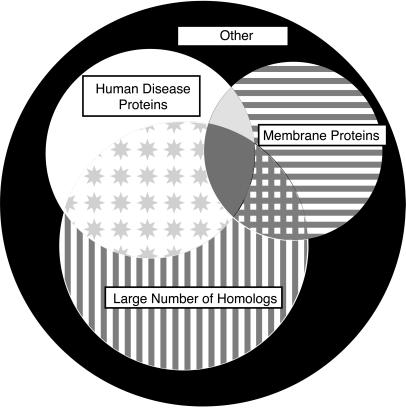
Figure 3.
The 2,681 ORFs of the genome of PA partitioned into homologs of human disease proteins (208, 8%, white region), membrane-spanning proteins (320, 12%, horizontal line region), and proteins having >4 homologs in other organisms (482, 18%, vertical line region). Attractive initial targets for structural genomics are proteins without transmembrane regions, with human disease relevance, and having many homologs in other genomes (422, 16%, star region). Additional ORFs had both >4 homologs in other organisms and transmembrane helix regions (102, 4%, crosshatch region), or both human disease homologs and transmembrane helix regions (60, 2%, light gray region). A few proteins had >4 homologs in other organisms, and human disease homologs and transmembrane helix regions (69, 3%, darker gray region). There are 1,018 ORFs belonging to none of these categories (37%, black region).