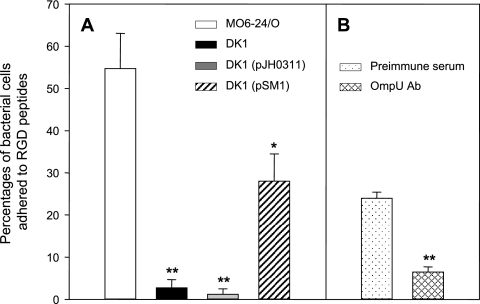
FIG. 6.
Role of OmpU protein in adherence of Vibrio vulnificus to immobilized RGD tripeptide. (A) Adherence of various V. vulnificus strains to the RGD tripeptide. V. vulnificus cells (wild-type V. vulnificus MO6-24/O [open bar], ompU mutant DK1 [closed bar], DK1 carrying pJH0311 [gray bar], and DK1 carrying a complementation plasmid, pSM1 [hatched bar]) were added to the 96-well plate coated with RGD tripeptide. Each well of the culture plate was coated with 20 μg of RGD tripeptide in PBS at 4°C for 18 h. V. vulnificus cells (1 × 105) were added to each of the RGD-coated wells and incubated at RT for 30 min. The percentage of bacterial cells that adhered to RGD-coated wells was determined by counting CFU of the eluted bacteria on LBS agar plates. Error bars represent the means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. Assay of binding of V. vulnificus to RGD tripeptide was performed in quadruplicate for each experiment. Asterisks indicate binding levels that were significantly different from that of wild-type V. vulnificus by Student's t test. Data with P values of <0.01 are indicated with two asterisks, whereas data with P values of between 0.01 and 0.05 are indicated with one asterisk. (B) Inhibition of RGD binding of wild-type V. vulnificus by anti-OmpU. The percentage of bacterial cells that adhered to RGD-coated wells was determined for wild-type V. vulnificus preincubated with mouse preimmune serum (dotted bar) or with anti-OmpU (cross-hatched bar) at 20 μg ml−1. Error bars represent the means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. Assay of binding of V. vulnificus to RGD tripeptide was performed in quadruplicate for each experiment. Asterisks indicate binding levels that were significantly different (P < 0.01) from that of wild-type V. vulnificus pretreated with mouse preimmune serum by Student's t test. Ab, antibody.