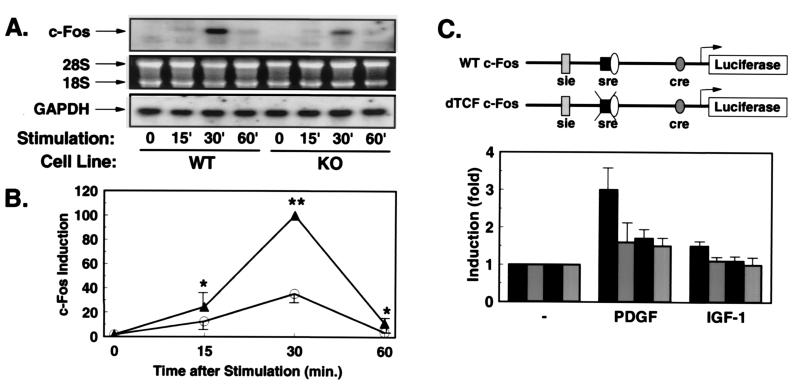
Figure 3.
Growth factor-stimulated expression of c-Fos is reduced in KO cells. (A) Northern blot analyses with c-Fos and GAPDH probes were performed on RNA extracted from WT or KO cells stimulated for the indicated times (min) with PDGF. The autoradiography after incubation with the c-Fos probe (Top). The integrity of RNA on the ethidium bromide-stained gel (Middle), and the autoradiography after hybridization with the GAPDH probe (Bottom). (B) Quantification was performed by densitometric scanning of the specific c-Fos signal/intensity of the GAPDH signal. Data are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments expressed as percentage of maximum intensity in WT cells (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (C) Schematic representation of the c-Fos promoter-luciferase constructs. WT c-Fos contains base pairs −734 to +43 of the human c-Fos gene cloned into promoterless luciferase gene (pGL2basic). In the construct δTCF-c-Fos, the binding site for TCF (base pair −320 to −328) was mutated (12). WT cells (black bars) and KO cells (gray bars) were cotransfected with the reporter plasmid WT c-Fos (black bars with white stippling) or the mutant reporter (gray bars with white stippling). After overnight culture in serum-free medium, cells were treated with PDGF or IGF-1 for 3 hr, and cell extracts were subsequently assayed for luciferase and β-galactosidase activity. Data represent the stimulation of luciferase activity/β-galactosidase activity in PDGF- and IGF-1-stimulated vs. untreated cells. Data are the mean of four separate experiments ± SEM.