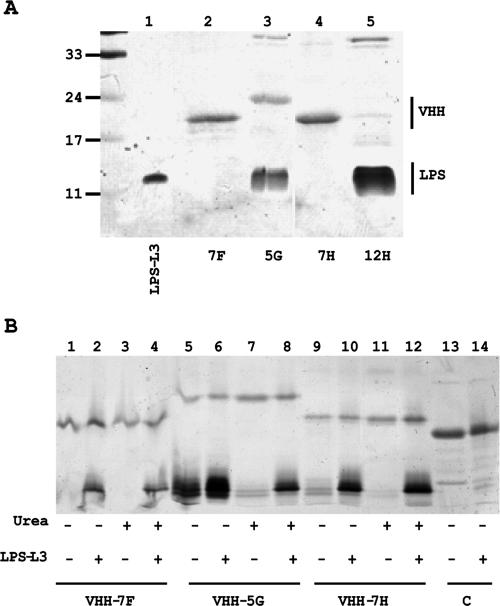
FIG. 1.
Characterization of the selected anti-LPS VHHs. (A) SDS-PAGE gel showing the copurification of E. coli LPS with VHHs. Purified VHHs were loaded on a 15% gel, and after electrophoresis the gel was stained first with silver for the presence of LPS and then with Coomassie brilliant blue to visualize proteins. Molecular mass marker proteins (in kDa) are indicated on the left, and L3 LPS from N. meningitidis was loaded in lane 1. (B) Binding of LPS after denaturation and renaturation of the VHHs. The purified VHHs indicated (lanes 1, 5, and 9) were denatured with urea (lanes 3, 7, and 11) to study the loss of bound E. coli LPS. The nondenatured VHHs (lanes 2, 6, and 10) and the denatured VHHs, which were allowed to renature in PBS (lanes 4, 8, and 12), were incubated with N. meningitidis L3 LPS. After the incubation, the VHH-Talon beads were pelleted and washed, and the LPS bound to the beads was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Binding of LPS to beads containing an irrelevant VHH was also analyzed (lanes 13 and 14). The gels were stained as described for panel A.