FIG. 4.
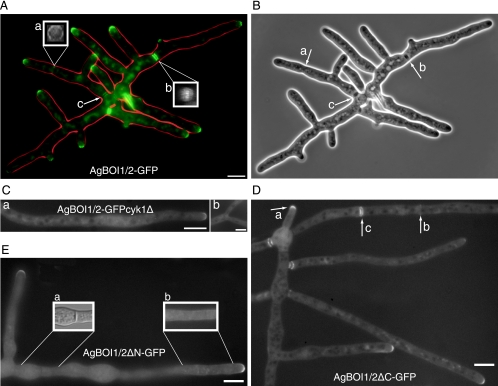
Localization of AgBoi1/2p. (A) Localization of wild-type AgBoi1/2p. Localization of the GFP signal is represented in green, and the hyphal periphery is in red. AgBoi1/2p-GFP is detected as a crescent at hyphal tips and as two different structures at sites of septation, either as a single ring at presumptive sites of septation (a) or as a double disc in mature septa (b). The two inserts (a and b) show three-dimensional reconstructed views of the indicated septal localizations. For each insert, a series of images was acquired along the z axis, and the planes were 90° rotated along the vertical axis. This gives a view along the hyphal tube onto the septum. (c) In mature septa, AgBoi1/2-GFP localization diminishes. (B) Phase-contrast image of that shown in panel A. Presumptive sites of septation identified from AgBoi1/2p-GFP ring localization are not yet visible (a), and mature septa identified from AgBoi1/2p-GFP disc localization are visible as black structures spanning the hyphae (b and c). (C) Localization of AgBoi1/2p-GFP in an Agcyk1Δ background. Septa are absent in the Agcyk1Δ strain, and AgBoi1/2p-GFP signal was observed neither in subapical regions (a) nor at sites of apical branching (b) where they are found in wild type. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Localization of AgBoi1/2pΔC. AgBoi1/2pΔC-GFP localizes at hyphal tips (a) and at septa as single-ring (b) or double-disc (c) structures as seen for the wild type. (E) Localization of AgBoi1/2pΔN. AgBoi1/2pΔN-GFP localizes only to hyphal tips and not to septa. (a) Nomarski illumination of the hyphal segment below. In the middle a septum is clearly visible but a GFP signal is lacking at the corresponding site. The GFP signal also appears to localize weakly over the entire cortex, as seen on insert b, which represents a brighter scaling of a single plane from the hyphal segment below. Bar, 10 μm.