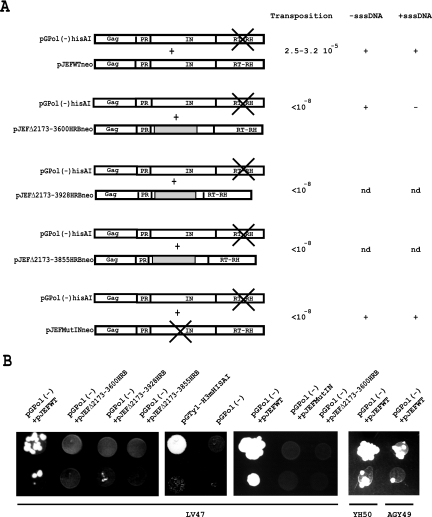
FIG. 4.
(A) Schematic representation of the Gag-Pol polyproteins expressed in yeast cells cotransformed with the pGPol(−) plasmid and the WT pJEF1105 plasmid (pJEF WTneo), the IN deletion mutant derivatives of pJEF1105 (pJEFΔ2173-3600HRB, pJEFΔ2173-3928HRB, and pJEFΔ2173-3855HRB), or the IN active-site mutant of pJEF1105 (pJEFMutIN). The deletions were filled in by inserting the yeast gene Hrb1 (gray rectangle) in order to avoid steric hindrance between the PR/IN and IN/RT cleavage sites and allow complete processing of the Gag-Pol polyprotein (37). In a previous study we showed that the deletion mutants Δ2173-3600 and Δ2173-3855 retained RT activity. The level of RT activity in Δ2173-3855 VLPs was low compared to that of WT or Δ2173-3600 VLPs. Transposition was induced at 22°C in a medium supplemented with 2% galactose and ended at 30°C in a medium containing 2% glucose. The fraction of His+ prototrophs was determined to calculate the frequency of transposition. The transposition frequency of a positive control with yeast cells containing the WT pGTy1-H3mHIS3AI plasmid was 1.2 10−3. Transposition of yeast cells cotransformed with pGPol(−) and WT pJEF1105 plasmids is decreased 30- to 40-fold (see text). Synthesis of -sssDNA and +sssDNA was determined by iterative primer extension. (B) Qualitative transposition assay in yeast strains LV47, YH50, or AGY49. A total of 10 μl of induced cells with an optical density at 600 nm of 1 to 1.5 and 10 μl of a 10-fold dilution were spotted onto glucose plates without histidine and incubated for 2 days at 30°C. A positive control with the WT pGTy1-H3mHIS3AI plasmid and a negative control with the pGPol(−)hisAI plasmid are shown.