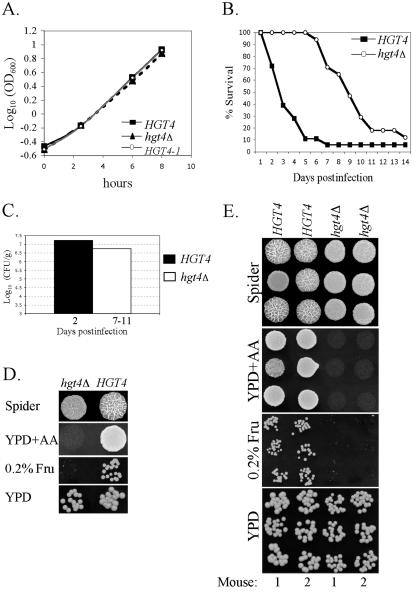
FIG. 8.
HGT4 is required for optimal virulence in vivo. (A) Growth curves for isogenic C. albicans strains. HGT4 (wild type: CM87 and CM97), hgt4Δ (null mutants: CM137 and CM140), and HGT4-1 (constitutive mutants: CM35 and CM36) cells were grown to log phase in liquid YPD aerated by shaking at 30°C. All standard deviations were <3% of the OD600 values. These C. albicans strains are isogenic and prototrophs, differing only in the HGT4 allele. (B) HGT4 affects virulence during disseminated candidiasis. Mice were injected in the lateral tail vein with 7.5 × 105 cells and monitored for morbidity and mortality. HGT4 indicates the hgt4Δ CM9 complemented with one copy of the wild-type gene, strain CM87 (n = 18), and hgt4Δ indicates the hgt4Δ CM9 complemented with the vector plus noncoding flanking regions of HGT4 (UTRs), strain CM137 (n = 17). (C) The fungal burden was determined for three mice infected with the HGT4 strain (day 2) and for three mice infected with the hgt4Δ strain (one mouse from day 7 and two mice from day 11). The variation between mice was 6 × 106 CFU/g (HGT4 strain) and 6 × 105 CFU/g (hgt4Δ strain). (D) Phenotypes for the original strains used to infect mice in the disseminated Candidiasis experiments in panel C: HGT4 (CM87) and hgt4Δ (CM137). (E) Phenotypes of individual clones recovered postmortem from the kidneys. C. albicans isolates were recovered from two mice infected with the HGT4 strain (day 2) and from two mice infected with the hgt4Δ strain (days 6 and 7). Three independent colonies from each mouse were tested for filamentation on spider medium, for growth on YPD-antimycin A, and for growth on synthetic complete medium with 0.2% fructose.