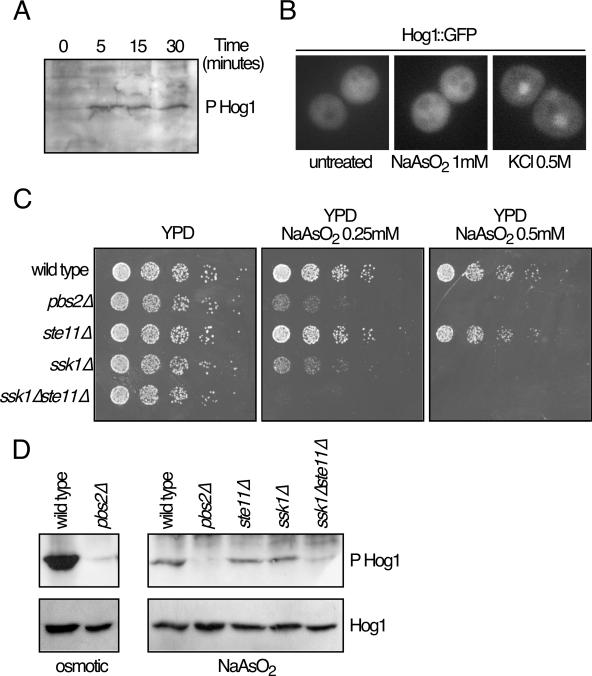
FIG. 2.
Hog1 phosphorylation and localization. (A) Hog1 phosphorylation (P Hog1) in response to arsenite. Western blotting analysis of yeast extracts (13) showed that Hog1 is phosphorylated after 0.5 mM sodium arsenite treatment for the indicated times. Hog1 phosphorylation was detected using specific anti-phosphorylated Hog1 protein. (B) Hog1 localization. Hog1-deficient cells were transformed with plasmid pRS-Hog1-GFP (5). Hog1::GFP protein expressed from this plasmid was detected after treatment with 0.5 M KCl or 1 mM sodium arsenite for 10 min. (C) Mutants in the Hog1 pathway show different sensitivities to sodium arsenite. Serial dilutions of the wild type and pbs2Δ, ste11Δ, ssk1Δ, and ssk1Δste11Δ mutant strains were plated in rich media containing several concentrations of sodium arsenite. Pictures were taken after 2 to 3 days at 24°C. (D) Phosphorylation of Hog1 in different mutants. Strains described for panel C were treated with KCl (0.8 M) for 10 min (osmotic) or sodium arsenite (1 mM) for 10 min (NaAsO2). Phosphorylation and abundance of Hog1 were monitored by Western blotting using specific polyclonal antibodies (9079; Santa Cruz).