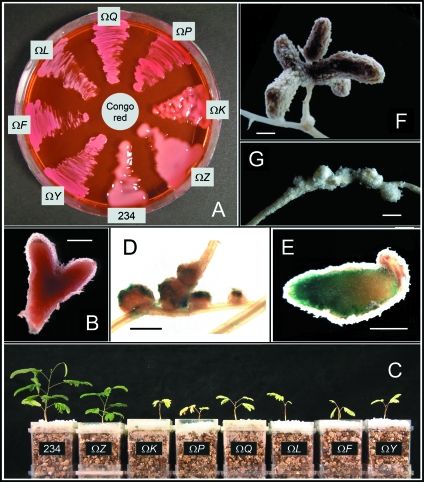
FIG. 2.
Phenotypes of Exo− mutants. (A) Parent strain NGR234 and Exo− mutants were grown on GMS agar plates containing 5% (wt/vol) sucrose and Congo red. NGRΩexoF (ΩF), NGRΩexoL (ΩL), NGRΩexoP (ΩP), NGRΩexoQ (ΩQ), and NGRΩexoY (ΩY) formed nonmucoid (“dry”) streaks and absorbed Congo red. NGR234 (234), NGRΩexoK (ΩK), and NGRΩexoZ (ΩZ) formed mucoid colonies. (B) Typical nitrogen-fixing nodule of L. leucocephala cv. Peru induced by NGR234 and harvested 92 days postinoculation. Nodules of L. leucocephala are often branched at this stage. (C) L. leucocephala cultivated in Magenta jars and inoculated with NGR234, as well as NGRΩexoF, NGRΩexoK, NGRΩexoL, NGRΩexoP, NGRΩexoQ, NGRΩexoY, and NGRΩexoZ. Plants were photographed 61 days postinoculation. Only nodules containing NGR234 and NGRΩexoZ fixed nitrogen. (D) Pseudonodules of L. leucocephala induced by NGRΩexoK expressing the gusA gene (42 days postinoculation; Fix− phenotype). Bacteria colonized the surface of pseudonodules, whereas GUS staining was not detected within pseudonodules. (E) Nitrogen-fixing nodule induced by a NGR234 derivative expressing the gusA gene (59 days postinoculation; Fix+ phenotype). Nodulated roots were stained for GUS activity. (F) Typical nodule of A. lebbek containing nitrogen-fixing bacteroids of NGR234 (87 days postinoculation; Fix+ phenotype). (G) Pseudonodules of A. lebbek induced by NGRΩexoK (87 days postinoculation; Fix− phenotype). Bars = 1 mm.