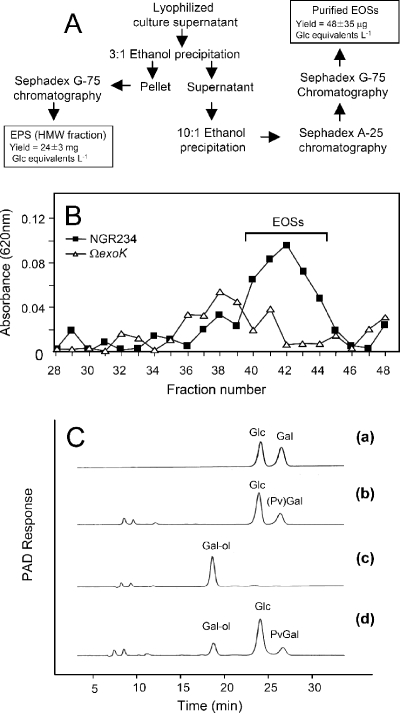
FIG. 4.
Characterization of EOSs. (A) Purification steps and yield of HMW forms of EPS and EOSs of NGR234. Bacterial supernatants were precipitated with ethanol in a stepwise fashion. EOSs were applied to a DEAE-Sephadex A-25 column in 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and eluted with 100 mM NaCl added to the same buffer. The final purification step was SEC on a Sephadex G-75 column. (B) SEC (Sephadex G-75) chromatography of EOSs. Fractions (1.5 ml) were collected, and the carbohydrates were analyzed using the anthrone method (absorbance at 620 nm). EOSs produced by NGR234 eluted in fractions 40 to 44. (C) Effect of NaBH4 reduction. HMW forms of EPS and EOSs were subjected to NaBH4 reduction and complete acid hydrolysis. Glc, Gal, and the resulting galactitol were analyzed by Dionex chromatography. Uronic acids were not analyzed. Chromatogram a shows the results for Glc and Gal standards. As shown in chromatogram b, purified HMW forms of EPS from NGR234 resulted in formation of Glc, PvGal, and Gal. PvGal and Gal coeluted [peak (Pv)Gal]. The ratio of Glc to (Pv)Gal was 5:2, as determined by integration of peak areas. As shown in chromatogram c, the Gal standard treated with NaBH4 was completely converted to galactitol. Chromatogram d shows that NaBH4 reduction of EOSs from NGR234 resulted in the formation of Glc, PvGal, and galactitol (PvGal/galactitol ratio, 1:1).