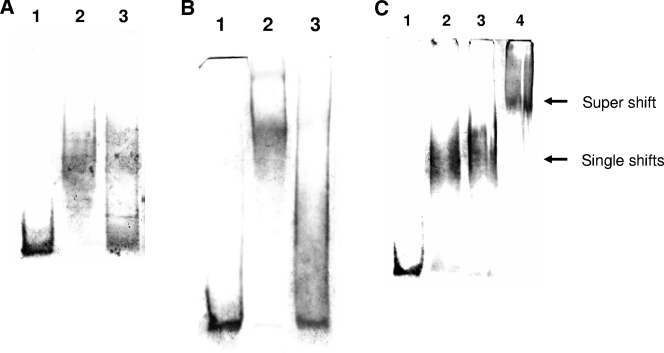
FIG. 2.
(A) EMSA with ScoC. Binding reactions were carried out with 10 nM DIG-labeled epr probe (∼150 bp) and ScoC (1 μM) in a 20-μl reaction buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.6, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM (NH4)2SO4, 1 mM dithiothreitol, Tween 20 (0.2% [wt/vol]), 30 mM KCl, 1 μg poly(dI-dC), and 0.1 μg poly-l-lysine at 37°C for 15 min. The bound product was electrophoresed on a 5% polyacrylamide gel in 0.25× Tris-borate-EDTA buffer at 4°C and electroblotted onto Nylon membrane, and DNA was detected with NBT/BCIP (Roche Applied Science; www.roche-applied-science.com/pack-insert/3353591a.pdf). Lane 1, DIG-labeled epr probe; lane 2, epr probe plus ScoC; and lane 3, epr probe plus ScoC plus 100× molar excess unlabeled probe. (B) EMSA with SinR (12 μM). (The binding conditions, electrophoresis, and detection method are as described for panel A. Lane 1, DIG-labeled epr probe (∼150 bp, 10 nM); lane 2, epr probe plus SinR; and lane 3, epr probe plus SinR plus 100× molar excess unlabeled probe. (C) EMSA with ScoC (1 μM) and SinR (12 μM). (The binding conditions, electrophoresis, and detection method are as described for panel A). Lane 1, DIG-labeled epr probe (∼150 bp, 10 nM); lane 2, epr probe plus ScoC; lane 3, epr probe plus SinR; and lane 4, epr probe plus ScoC plus SinR.