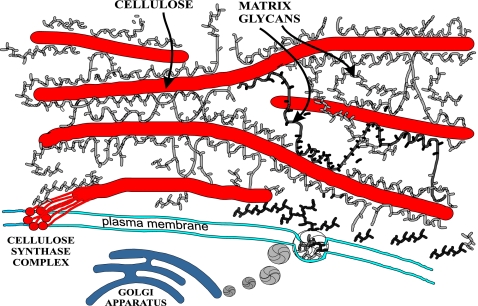
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the plant cell wall. Cellulose microfibrils are synthesized by large complexes in the plasma membrane and are glued together by branched matrix polysaccharides synthesized in the Golgi and deposited by vesicles along the inner surface of the cell wall. The ≈4-nm-wide cellulose microfibril in cross-section consists of ≈36 β-(1→4)-d-glucans organized into a crystalline array. Polysaccharides such as arabinoxylan and xyloglucan spontaneously bind to the surface of cellulose and may also be entrapped during coalescence of the β-(1→4)-d-glucans to form the microfibril. Hydrophilic pectins and structural proteins (data not shown) also make up the matrix between cellulose microfibrils and influence the wall's physical properties (7).