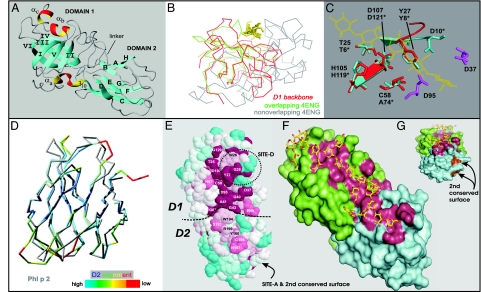
Fig. 2.
Structure of EXPB1 (PDB ID code 2HCZ). (A) Ribbon model of EXPB1 showing the overall configuration of the two domains. (B) Superposition of the peptide backbone of EXPB1 D1 (shown entirely in red) with the peptide backbone of Humicola Cel45 (PDB ID code 4ENG), colored green for regions of good alignment with EXPB1 and gray otherwise. The yellow residues indicate cellohexaose from the 4ENG model. (C) Superposition of residues making up the catalytic site of Humicola Cel45 (blue) and corresponding residues of EXPB1 (red). Other conserved acidic residues in this region of EXPB1 are shown in purple. (D) Superposition of EXPB1 D2 (colored) and Phl p 2 (gray), a group-2/3 grass pollen allergen (PDB ID code 1WHO). Coloring scale from best to poorest alignment of peptide backbones is shown at the bottom. (E) Top view of the conserved surface of EXPB1, color-coded to indicate conservation (red, most conserved; blue, least conserved; white, intermediate). Conserved residues are labeled, and the locations of two antigenic epitopes are indicated (SITE-D and SITE-A). (F) A model of glucurono-arabinoxylan (yellow and red) was manually fitted to the long open groove of EXPB1 by using the program O (66) and subsequently energy-minimized by using the program CNS (67). Green residues are from D1, cyan residues are from D2, and red residues are the conserved residues identified in E. (G) End view of same model as in F. The image in E was generated from the program CONSURF (68) by using the alignment of 80 EXPB proteins in the GenBank database and 2HCZ after removal of the N-terminal extension. The images in G and F were generated with PYMOL (DeLano Scientific) after removal of the N-terminal extension.