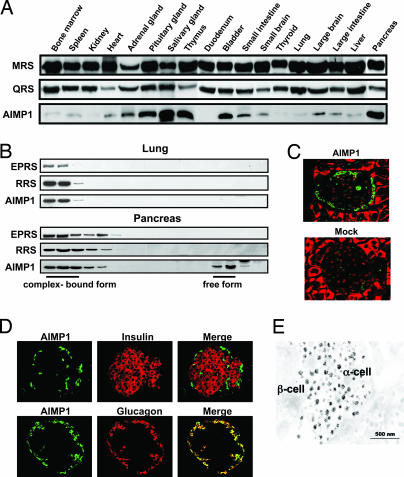
Fig. 1.
Enriched localization of AIMP1 in pancreatic α cells. (A) Tissue-dependent variations of protein levels were determined for AIMP1 and two tRNA synthetases, methionyl-tRNA synthetase and glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase, which are components of the multi-tRNA synthetase complex. Proteins extracted from each tissue were subjected to Western blot analysis with their respective antibodies. (B) AIMP1 was separated into the portions that were bound and unbound to the multi-tRNA synthetase complex by size exclusion chromatography. The proteins extracted from the lung and pancreas that contained low and high levels of AIMP1, respectively, were compared. The two other components for the complex, glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase and arginyl-tRNA synthetase, were used as indicators for the complex-bound portion. The eluted proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE, and three proteins were detected with their respective antibodies. (C) Localization of AIMP1 in the pancreatic islet was determined by immunofluorescence staining. AIMP1 and nuclei were stained green with FITC-conjugated antibody and red with propidium iodide, respectively. (Magnification: ×20.) (D) Colocalization of AIMP1 (green) in the pancreatic α cells with glucagon (red) under a confocal microscope. In Upper, pancreatic β cells were stained with insulin antibody and rhodamine-conjugated secondary antibody. (Magnification: ×20.) (E) A mouse pancreas was dissected and fixed as described in Materials and Methods. Grids were reacted with anti-AIMP1 antibody and detected with colloidal gold-conjugated protein A. The labeled sections were observed under an electron microscope (JEOL) at 80 kV.