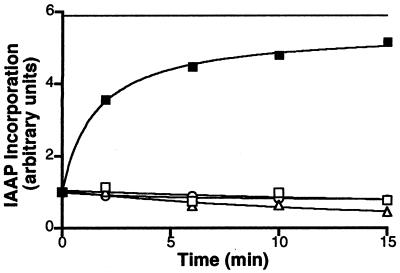
Figure 4.
Recovery of IAAP binding to the Pgp⋅8AzidoADP⋅Vi complex requires ATP hydrolysis. Crude membranes (1 mg/ml protein) were treated with 1.25 mM 8AzidoATP and 250 μM Vi for 10 min at 37°C in the ATPase assay buffer (see Materials and Methods). The reaction was stopped by placing the samples on ice. Excess 8AzidoATP and Vi were removed by centrifugation at 300,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The pellet was resuspended in 40 mM Mes⋅Tris, pH6.8, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM sodium azide, 2 mM EGTA, and 2 mM DTT and divided into five aliquots to which the following additions were made: 10 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM AMPPNP (▵), 10 mM MgCl2, and 1.2 mM ATP (■), 5 mM EDTA (□), and 250 μM Vi (○). The continuous horizontal line shows the extent of IAAP incorporated into an equivalent amount of untreated control membranes, which were processed in parallel. The samples were incubated at 37°C, and aliquots were removed at the indicated intervals, placed on ice, and photocrosslinked with IAAP. After SDS/PAGE, the radioactivity associated with the Pgp was estimated by PhosphorImager analyses and normalized such that the radioactivity in the untreated sample at 0 min was 1. The data are representative of three independent experiments.