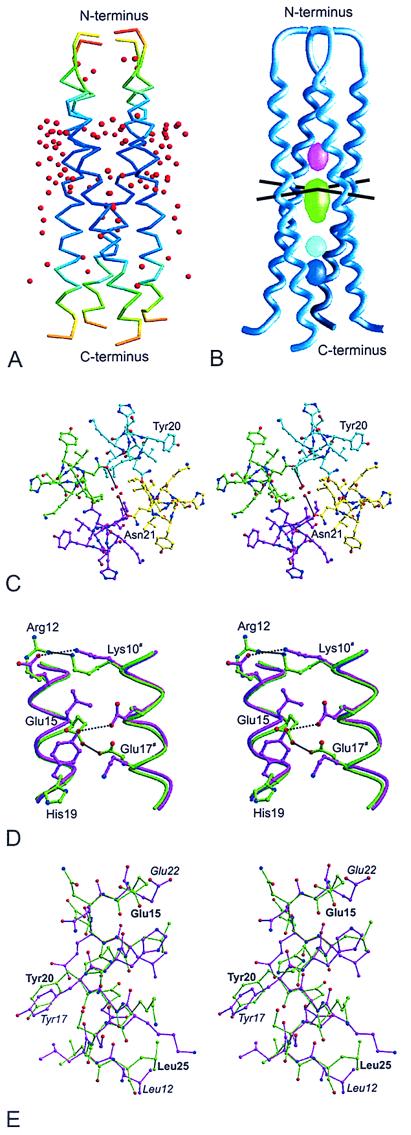
Figure 2.
(A) Backbone of the r-GCN4-p1′ tetramer colored according to temperature factor (dark blue = 20 Å2; red = 100 Å2). Water molecules are shown as red bullets. Figures were prepared with the programs molscript and bobscript (18, 19). (B) Cavities in the r-GCN4-p1′ structure. The volumes of the cavities are 87 Å3 (green), 39 Å3 (blue), 36 Å3 (magenta), and 30 Å3 (cyan). The cavities were calculated with a probe radius of 1.6 Å. The palindrome axis intersects the 4-fold symmetry axes at the top of the large cavity; axes are indicated as black lines. The figure was generated with the program grasp (22). (C) Stereo projection of water molecules in the central cavity. The view is parallel to the 4-fold symmetry axis. Possible hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines. (D) Polar interactions on the surface of r-GCN4-p1′ (green carbon atoms) and GCN4-pLI mutant (pink carbon atoms). Polar interactions are indicated by black lines. Residue numbering corresponds to the r-GCN4-p1′ structure; # refers to the next repeat. (E) Superposition of residues 15–25 of the r-GCN4-p1′ structure (green carbon atoms) onto residues 12–22 of the wild-type GCN4-p1 structure (pink carbon atoms, residue numbers in italics). The Cα atoms superimpose with an rmsd of 0.29 Å. In the r-GCN4-p1′ structure, the direction of the sequence is from top to bottom. In the GCN4-p1 structure, the direction is from bottom to top.