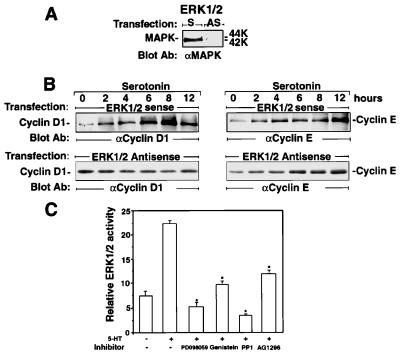
Figure 3.
MAPK regulates cyclin D1 but not cyclin E levels in the 5-HT2B receptor mitogenic signaling and is regulated by tyrosine kinases. (A) Depletion of MAPK by antisense transfection. LM6 cells were transfected transiently with antisense (AS) or sense (S) oligonucleotides of mouse MAPK (ERK1/2) mRNA and probed with MAPK antibody. (B) 5-HT-induced cyclin D1 expression, but not that of cyclin E, is abolished in MAPK-depleted cells. After visualization with anti-cyclin D1 antibody, the membranes were washed and reprobed with cyclin E antibody. The positions of cyclin E and cyclin D1 are indicated. (C) MAPK activation is regulated by tyrosine kinases. After pretreatment with inhibitors for MAPK kinase (15 μM PD 098059), tyrosine kinase (15 μM genistein), Src (1 μM PP1), and PDGFR (0.1 μM AG 1296), the cells were incubated with 5-HT (1 μM) for 10 min, then revealed with anti-active MAPK antibody. After being revealed by enhanced chemiluminescence, the relative active ERK1 and ERK2 protein levels were assessed by using a luminometer. The stars indicate significant inhibition of the parameters as compared with 5-HT stimulation alone (P < 0.05; n > 3).