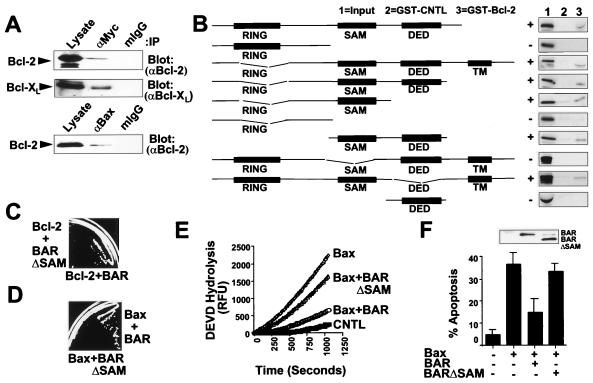
Figure 3.
SAM Domain of BAR Is Required for Interaction with Bcl-2 and Inhibition of Bax-Induced Apoptosis. (A) 293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-BAR(ΔR) and either Bcl-2 or Bcl-XL (Upper) or with plasmids encoding Bax and Bcl-2 (Lower). Cells were lysed 2 days later in buffer containing 0.4% Nonidet P-40, and immunoprecipitations were performed by using anti-Myc or anti-Bax antibodies or by using mouse IgG1 as a control. Immune complexes and lysates (representing ≈5% of input) were subjected to SDS/PAGE and immunoblot analysis by using antisera for detection of Bcl-2 or Bcl-XL. (B) For in vitro binding studies, in vitro translated 35S-labeled BAR mutant proteins were incubated with 10 μg of either GST-Bcl-2 or GST (control; CNTL) recombinant proteins, and protein complexes were recovered on glutathione-Sepharose and analyzed by SDS/PAGE followed by autoradiography. In vitro translation mixes (10% input) were run directly in gels as a control. A wide variety of control GST proteins were tested, thus confirming specificity of BAR interactions with Bcl-2 (not shown). All BAR fragments shown were >50% intact when produced by in vitro translation in reticulocyte lysates, but others attempted could not be produced without extensive degradation, such as SAM only. (C) For yeast two-hybrid assay, 1 μg pGilda-Bcl-2(ΔTM) was cotransformed into EGY191 cells with 1 μg pJG4–5-BAR or pJG4–5-BAR(ΔSAM). Transformants were initially selected on glucose-containing medium lacking histidine and tryptophan. Two-hybrid interactions were assayed by streaking onto galactose plates lacking leucine, histidine, and tryptophan. Use of various positive and negative control proteins in yeast two-hybrid assays confirmed the validity of these observations (not shown). (D) For cytotoxicity assays in yeast, plasmids encoding BAR or BAR(ΔSAM) were transformed into a yeast strain harboring YEp51-Bax. Transformants were then streaked on galactose-containing synthetic medium lacking tryptophan and leucine. Photograph was taken after 4 days at 30°C. (E) For caspase assays, 293T cells were transfected with either 4 μg of vector control plasmid (CNTL) or with 0.5 μg Bax-encoding plasmid together with 3.5 μg of either vector control plasmid or plasmids encoding BAR or BAR(ΔSAM). Cell extracts were prepared 24 hr after transfection, normalized for protein content (25 μg), and incubated with 100 μM DEVD-AFC. Enzyme activity was determined by the release of the AFC fluorophore (expressed as relative fluorescence units, RFU). (F) A portion of the transfected 293T cells described in E were stained with DAPI, and the percentage of GFP-positive cells with fragmented or condensed nuclei (apoptotic) was determined (mean ± SD; n = 3). Inset shows immunoblot analysis of lysates from transfected cells using anti-BAR antiserum with enhanced chemiluminescence-based detection.