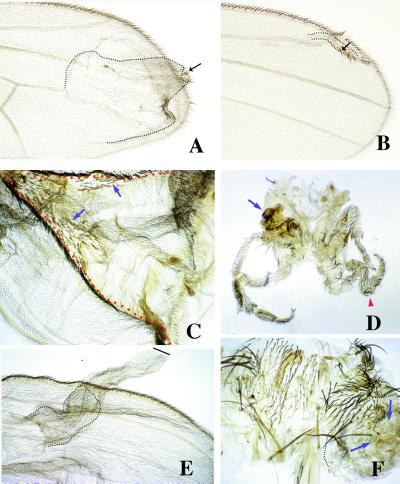
Figure 1.
Adult phenotypes caused by clones of ectopic expression of Nintra using the abx/Ubx promoter (A and B) and Dl by using the actin promoter (C–F). In A and B, clones of Nintra-expressing cells (forked) in the wing blade cause the ectopic differentiation of wing margin structures (arrows) and induce the proliferation of wild-type cells surrounding the clone (dotted line). The clones generated close to the a/p boundary and away from the d/v boundary cause larger outgrowths (A) than clones close to the d/v border (B). In C, a clone (red dotted line) of Dl-expressing cells (yellow) in the dorsal compartment causes wing outgrowths that contain wing margin structures at the clone boundaries (arrows indicate mutant elements). (D) Large outgrowths in the legs associated with clones of Dl-expressing cells (arrow indicates a large outgrowth in the coxal region and arrowhead, an enlarged leg). In E, clones of Dl-expressing cell in the ventral compartment of the wing cause large outgrowth that is not associated with the differentiation of wing margin structures. The wild-type cells constitute only a small fraction of the outgrowth (dotted line). (F) Large outgrowth (dotted line) in the notum caused by a clone (arrows) of Dl-expressing cells.