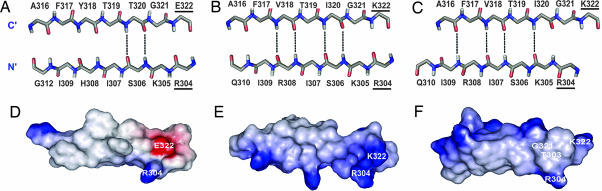
Fig. 3.
The influence of the sequence and residue-pairing in the V3 β-hairpin on the electrostatic potential at the base of the hairpin. (A) The residue pairing and hydrogen bonds in the schematic structure of V3JR-FL bound to 447-52D Fv. (B) The residue pairing and hydrogen bonds in the schematic structure of the V3IIIB bound to the 447-52D Fv. (C) The residue pairing and hydrogen bonds in V3IIIB bound to 0.5β Fv. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by black dashed lines. (D–F) Electrostatic potential map calculated by the DELPHI program in different V3 structures: V3JR-FL bound to 447-52D Fv (D) and V3IIIB bound to 447-52D Fv (E). Residues R304 and K322 were modeled according to the conformation of V3JR-FL bound to 447-52D Fv (the R5 conformation of V3). (F) V3IIIB bound to 0.5β Fv; residues T303 and K322, not included in the NMR structure, were modeled. The charged residues involved in the switch between the R5 and X4 conformation are underlined. Positive potential is shown in blue, and negative potential is shown in red.